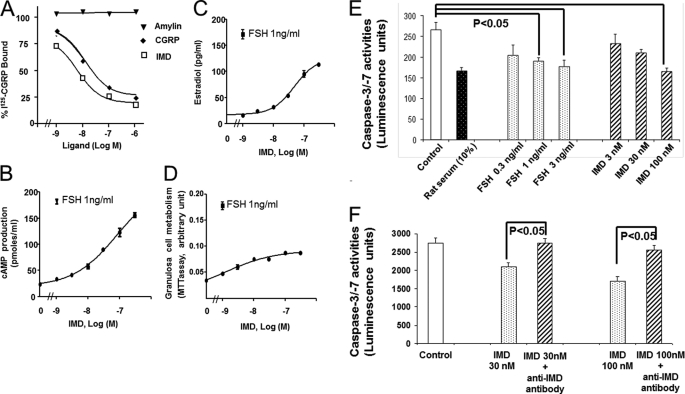
FIGURE 2.
IMD/ADM2 increased survival of granulosa/cumulus cells cultured in vitro. A, competitive receptor-binding analysis using isolated granulosa/cumulus cells from immature 26-day-old rats primed with diethylstilbestrol (DES) for 4 days. Each data point represents the mean ± S.E. of triplicate samples. B and C, dose-dependent stimulation of cAMP (B) and estradiol (C) production by IMD and FSH in isolated granulosa/cumulus cells. Cell cultures were treated with different hormones in a serum-free condition for 16 h. Each data point represents the mean ± S.E. (error bars) of quadruplicate samples. D, dose-dependent stimulation of 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) conversion by IMD and FSH in cultured granulosa/cumulus cells. E, dose-dependent inhibition of granulosa/cumulus cell caspase-3 and -7 activities by IMD and FSH. The activities of caspases were determined using a Caspase-Glo 3/7 luminescent assay (Promega) at 24 h after culture. Cultures treated with 10% rat serum were used as positive controls. F, the anti-apoptosis effect of IMD (represented by an inhibition of caspase-3 and -7 activities) was neutralized by coincubation with an anti-IMD antibody (n = 4). *, significantly different from controls (p < 0.05). Similar results were obtained in three separate experiments.