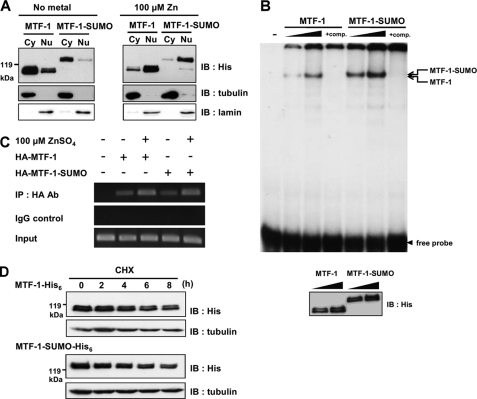
FIGURE 3.
Effect of sumoylation on nuclear translocation, MRE-binding activity, and stability of MTF-1. A, MTF-1-His6 or MTF-1-SUMO-His6 were transfected into CHO K1 cells with or without 100 μm zinc treatment for 3 h. Cytosolic (Cy) and nuclear (Nu) extracts were prepared and the expressed proteins were analyzed with Western blot. Tubulin and lamin were used as cytosolic and nuclear markers, respectively. B, MTF-1-His6 or MTF-1-SUMO-His6 were transfected into CHO K1 cells and whole cell extracts were prepared for EMSA with increasing amounts of cell extracts. Unlabeled MREs were used as a competitor to show the specificity of MTF-1/MREs binding. The amount of expressing protein applied to EMSA was analyzed by Western blot with anti-His6 antibodies (lower panel). C, HA-MTF-1 or HA-MTF-1-SUMO were transfected into HEK293 cells with or without 100 μm zinc treatment for 3 h. ChIP assay was conducted to investigate the protein-DNA interaction in vivo and the PCR-amplified fragments of human MTIIA promoter shown. Normal rabbit IgG was used as the control of the assay. D, MTF-1-His6 or MTF-1-SUMO-His6 were transfected into CHO K1 cells. Following administration of 50 μm cycloheximide (CHX) for various time intervals, the quantities of MTF-1 were detected by immunoblotting (IB). Tubulin was employed as loading control.