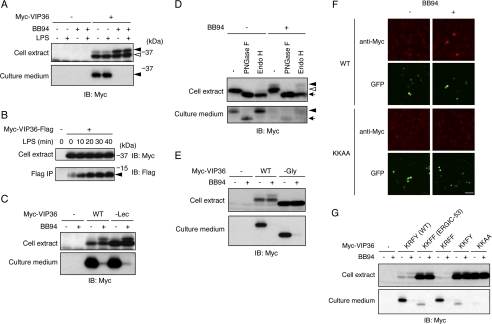
FIGURE 2.
VIP36 is a shedding target. A, N-terminally Myc-tagged VIP36 was expressed in Raw 264.7 cells, and cells were treated with BB94 and/or LPS as indicated. Both cell extracts (top panel) and culture supernatants (bottom panel) were subjected to Western blotting with an anti-Myc antibody. Closed arrowheads indicate the shedding-susceptible form of VIP36 (top panel) and a soluble form of VIP36 (bottom panel), respectively. An open arrowhead indicates the shedding-resistant form of VIP36. B, cytoplasmic FLAG-tagged VIP36 was expressed in Raw 264.7 cells, and cells were treated with LPS for the indicated times. Cell extracts (top panel) and anti-FLAG immunoprecipitates (bottom panel) were subjected to Western blotting (IB) with anti-Myc and anti-FLAG antibodies, respectively. A closed arrowhead indicates the membrane-bound fragment of VIP36. C, a Myc-tagged lectin-defective mutant of VIP36 (−Lec) was expressed in Raw 264.7 cells. Cells were treated with or without BB94, and cell extracts (top panel) and culture supernatants (bottom panel) were subjected to Western blotting with an anti-Myc antibody. D, Myc-tagged VIP36 was expressed in Raw 264.7 cells, and cell extracts (top panel) and culture supernatants (bottom panel) were digested by deglycosylation enzymes as indicated and subjected to Western blotting with an anti-Myc antibody. Closed and open arrowheads in the top panel indicate Endo H-resistant and Endo H-sensitive glycoforms of VIP36, respectively. The arrow in the top panel indicates the deglycosylated form of VIP36. A closed arrowhead and an arrow in the bottom panel indicate the Endo-H-resistant glycoform and deglycosylated form of soluble VIP36, respectively. PNGase F, peptide N-glycosidase F. E, a Myc-tagged glycosylation-defective mutant of VIP36 (−Gly) was expressed in Raw 264.7 cells. Cells were treated with or without BB94, and cell extracts (top panel) and culture supernatants (bottom panel) were subjected to Western blotting with an anti-Myc antibody. F, Raw 264.7 cells expressing Myc-tagged wild-type VIP36 (WT) or C-terminal KKAA mutant of VIP36 (KKAA) were treated with BB94 for 1 h and subjected to cell surface staining using anti-Myc antibody (anti-Myc). Transfected cells were identified as GFP-positive cells (GFP). Bar, 50 μm. G, Myc-tagged C-terminal substitution mutants of VIP36 were expressed in Raw 264.7 cells. Cells were treated with or without BB94, and cell extracts (top panel) and culture supernatants (bottom panel) were subjected to Western blotting with an anti-Myc antibody.