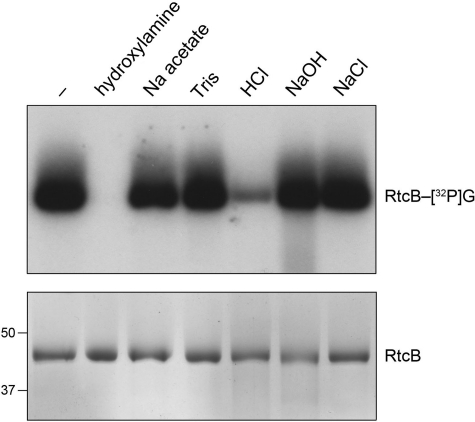
FIGURE 10.
Chemical stability of the RtcB-[32P]guanylate adduct. Reaction mixtures (140 μl) containing 50 mm Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 10 μm [α-32P]GTP, 2 mm MnCl2, and 5 μm RtcB were incubated at 37 °C for 1 min. The mixtures were then adjusted to 0.5% SDS and 5 mm EDTA. Aliquots (20 μl) were withdrawn and either received no further additives (lane −) or were adjusted to 600 mm hydroxylamine (pH 5.0) or 600 mm sodium acetate (pH 5.0), and then incubated at 37 °C for 30 min. Additional aliquots (20 μl) were withdrawn and adjusted to either 150 mm Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), 150 mm HCl, 150 mm NaOH, or 150 mm NaCl; these samples were heated at 75 °C for 5 min; the HCl-treated sample was neutralized by addition of NaOH to 150 mm and the NaOH-treated sample was neutralized by adding HCl to 150 mm. The samples were supplemented with 20 μl of a solution containing 100 mm Tris (pH 6.8), 10 mm EDTA, 200 mm DTT, 4% SDS, 20% glycerol, 0.2% bromphenol blue. One-half of each sample was analyzed by SDS-PAGE, followed by autoradiography of the dried gel to visualize the RtcB-[32P]guanylate adduct (top panel). The other half of each sample was analyzed by SDS-PAGE, and the gel was stained with Coomassie Blue dye to visualize the RtcB polypeptide (bottom panel); the positions of 50- and 37-kDa pre-stained marker proteins are indicated on the left.