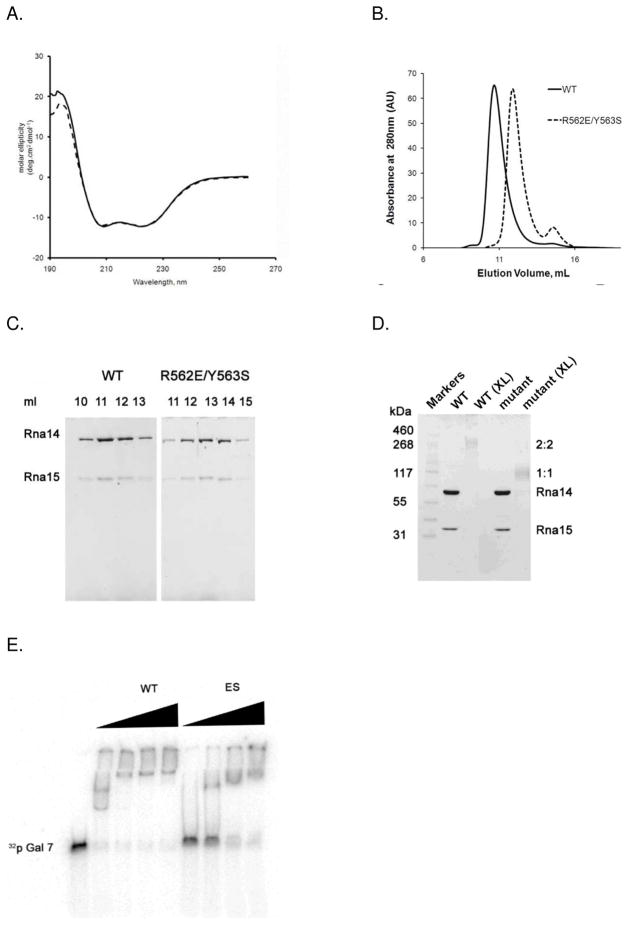
Figure 2.
Disruption of the Rna14 homodimer interface. A. CD spectra of WT (solid line) and ES mutant (dashed line) Rna14/Rna15 complex. B. Size exclusion chromatograms of WT and ES mutant Rna14/Rna15 complexes applied onto a Superdex-200 HR10/30 column. The WT Rna14/15 complex elutes as a single peak at 11 ml, corresponding to the molecular weight of about 380 kDa. ES mutant complex elutes at 13 ml, corresponding to a molecular weight of 205 kDa. C. SDS-PAGE analysis of the WT and ES mutant Rna14/Rna15 complex peak fractions showing that Rna15 is retained in both complexes. D. Formaldehyde cross-linking of WT and ES mutant Rna14/Rna15 complex. Samples denoted (XL) have been cross-linked with 0.5% formaldehyde. E. EMSA analysis of GAL7 RNA binding. ES Rna14/Rna15 mutant still binds the GAL7 RNA substrate, however with weaker affinity.