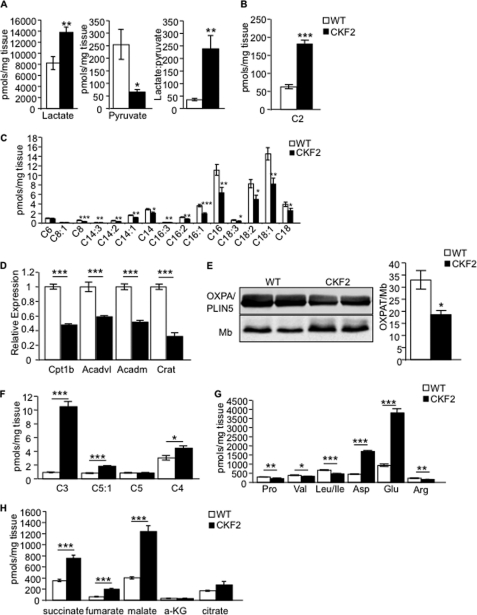
FIGURE 7.
CKF2 mice have altered fuel utilization in skeletal muscle. A, CKF2 mice exhibited increased levels of lactate and decreased levels of pyruvate. The lactate/pyruvate ratio indicated that CKF2 had increased glycolysis. B, we observed a significant increase in C2-carnitine (acetylcarnitine) levels supporting increased glycolysis and oxidation in the TCA cycle. C, medium and long chain acylcarnitine species were decreased in CKF2 mice, indicating decreased fatty acid oxidation. D, muscles of CKF2 mice show significantly decreased expression of genes encoding proteins involved in fatty acid oxidation (carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1β (Cpt1b); very long chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (Acadl); medium chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (Acadm); carnitine O-acetyltransferase (Crat)). E, Western blot analysis indicates that CKF2 mice have decreased levels of the PPARα target perilipin 5/OXPAT in quadriceps. Data are represented as mean ± S.E.; n = 3 mice per genotype; *, p < 0.01. Mb, myoglobin. F, odd chain acylcarnitine species derived from oxidation of BCAAs were significantly increased in CKF2 mice. G, decreased concentrations of BCAA in skeletal muscles of CKF2 mice. H, increased TCA cycle intermediates in skeletal muscle of CKF2 mice. a-KG, α-ketoglutarate. Data in all panels are represented as mean ± S.E.; n = 5 mice per genotype. *, p < 0.01; **, p < 0.001; ***, p < 0.0001.