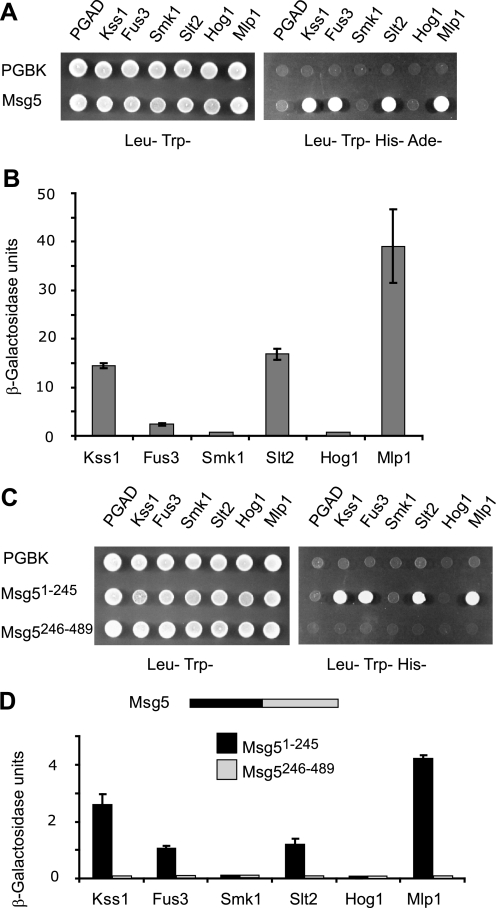
FIGURE 1.
Interaction of Msg5 with MAPKs. A, qualitative analysis of two-hybrid interaction by growth analysis of diploid yeast cells transformed with plasmids encoding the indicated proteins. Vector pGBKT7 (bearing the Gal4 DNA-binding domain) or pGBKT7-Msg5 was transformed into PJ69-4A S. cerevisiae strain and mated with PJ69-4α S. cerevisiae strain transformed with plasmid pGADT7 (bearing the Gal4 activation domain, pGADT7-Kss1, pGADT7-Fus3, pGADT7-Smk1, pGADT7-Slt2, pGADT7-Mlp1, or pGADT7-Hog1. Yeast diploids were spotted onto SD medium lacking leucine and tryptophan (left) or SD medium lacking leucine, tryptophan, histidine, and adenine (right). Cell growth on the latter medium provides evidence for the occurrence of protein-protein interaction. B, semiquantitative analysis of the two-hybrid interaction between Msg5 and the distinct MAPKs based on the level of induction of β-galactosidase. Experiments were performed in triplicate on the diploid strains described in A, with error bars representing S.D. C, qualitative analysis of the two-hybrid interaction between the N-terminal Msg5 (Msg5(1–245)) or C-terminal Msg5 (Msg5(246–489)) region and the different MAPKs. Before mating, pGBKT7, pGBKT7-Msg5(1–245) or pGBKT7-Msg5(246–489) were transformed into PJ69-4A cells, and pGADT7, or pGADT7-Kss1, pGADT7-Fus3, pGADT7-Smk1, pGADT7-Slt2, pGADT7-Mlp1, or pGADT7-Hog1 were transformed into PJ69-4α cells. Two-hybrid assays were performed as indicated in A. D, semiquantitative analysis of the two-hybrid interaction between the same Msg5 protein fragments as in C and the different MAPKs. A schematic showing both halves of Msg5 is also displayed. Experiments were performed in triplicate on the diploid cells described in C, with error bars representing S.D.