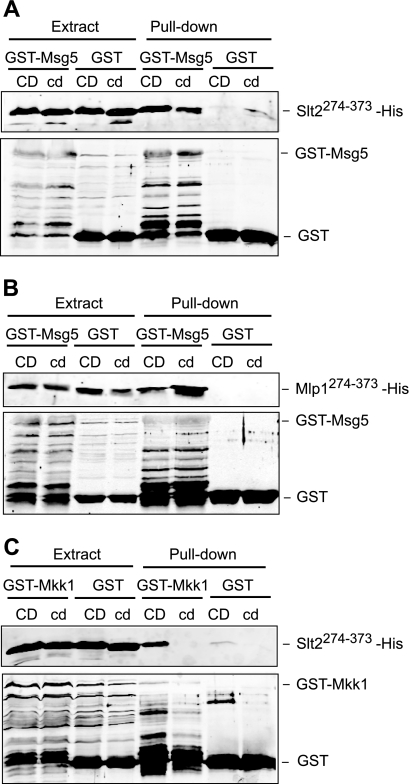
FIGURE 7.
Involvement of the common docking domain of Slt2 and Mlp1 on binding to distinct interactors. A, Western blot analysis of the in vitro co-purification of recombinant Msg5 with the indicated Slt2 fragments. E. coli extracts containing GST or GST-Msg5 were incubated with E. coli extracts containing Slt2(274–373)-His (CD) or Slt2(274–373)(323N,326N,327N)-His (cd) and glutathione-Sepharose to pull down GST complexes. Immunodetection was performed using anti-poly-His (top) and anti-GST (bottom) antibodies. B, Western blot analysis of the in vitro co-purification of recombinant Msg5 with the indicated Mlp1 fragments. E. coli extracts containing GST or GST-Msg5 were incubated with E. coli extracts containing Mlp1(274–373)-His (CD) or Mlp1(274–373)(326N)-His (cd) and glutathione-Sepharose to pull down GST complexes. Immunodetection was performed as in A. C, Western blot analysis of the in vitro co-purification of recombinant Mkk1 with the indicated Slt2 fragments. E. coli extracts containing GST or GST-Mkk1 were incubated with E. coli extracts containing Slt2(274–373)-His (CD) or Slt2(274–373)(323N,326N,327N)-His (cd) and glutathione-Sepharose to pull down GST complexes. Immunodetection was performed as in A. In all cases, reproducible results were obtained in different experiments, and selected images correspond to representative blots.