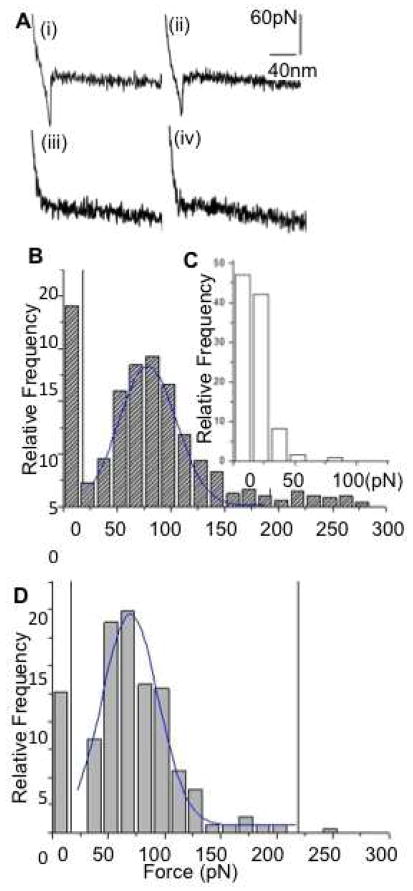
Figure 4.
Biochemical characterization of human salivary exosomes via force spectroscopy showing quantitative differences between CD63 surface receptors density (a) Typical curves showing force (pN) as a function of separation (nm) for a single pull with (i) adhesive event between cancer exosomes and (ii) normal exosomes probed with antiCD63 functionalized tip. (iii)– (iv) show weak or no binding between nonspecific antibody functionalized tip with cancer and normal exosomes respectively. (b) Histogram of rupture events (relative frequency versus rupture force in pNs) shows specific CD63 antibody-induced forces were distributed in the range of 30–200 pN. Sampled forces (n~500 each) from six normal and six oral cancer patient saliva exosome had each data point representing a single force measurement at any position on the exosomes surface (bin size 15 pN) (c) Nonspecific interactions were observed mostly at <50 pN.