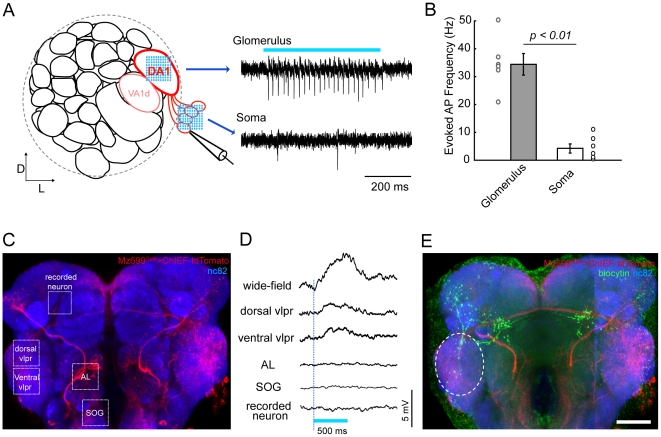
Figure 5. Specific activation of ChIEF-expressing neurons in transgenic Drosophila brain.
(A) Schematic illustration of one antennal lobe in the Drosophila brain (left). Three glomeruli (DA1 and VA1d are dash circled, with DC3 beneath them) are labeled in the Mz19-Gal4 line, and the projection neurons (PNs) of the DA1 glomerulus are shown in red. Loose-patch recordings were made on DA1 PNs while laser scanning stimulation was provided either on the glomerulus or on the soma. Spike trains could be reliably evoked when stimulating the glomerulus but not when stimulating the soma (right). (B) Laser stimulation on the glomerulus is more capable of activating PNs than stimulation on the soma (n = 6, error bars: SEM). (C) Fluorescent image of a brain of a Mz699-Gal4>UAS-ChIEF-tdTomato transgenic fly. Cells expressing ChIEF are shown in red, and the whole brain was counterstained with the synaptic marker mAb nc82 to visualize brain structures (blue). Different stimulation sites are indicated by the white dashed boxes. (D) Membrane potential changes were measured by whole-cell recording while light stimulation was provided (Blue bar, duration of the laser stimulation). Significant depolarizations could be evoked by wild-field blue light illumination or laser stimulation on the ventrolateral protocerebrum (VLPR), but not on the antennal lobe (AL), the sub-esophageal ganglia (SOG), or the recorded neuron. (E) Post-hoc staining of the recorded neuron (green) showed the morphological overlap between the recorded neuron and the candidate upstream ChIEF-expressing neurons (white dashed ellipse). Scale bar, 20 µm.