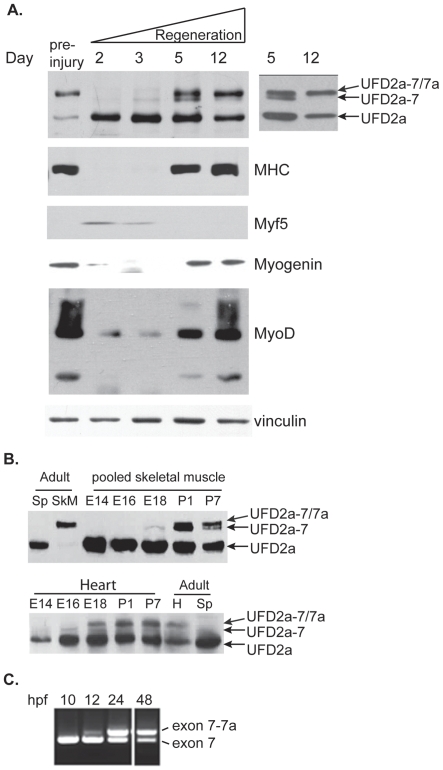
Figure 6. Expression of UFD2a alternative-splice forms occurs sequentially during regeneration and developmental myogenesis.
A). Mice received intramuscular injections of cardiotoxin (CTX) in the right tibialis anterior muscle. After the indicated number of days of recovery, the treated and untreated contralateral muscles were harvested and analyzed by immunoblotting for UFD2a, the mature muscle marker myosin heavy chain (MHC), the proliferating myoblast marker Myf5, myogenin, MyoD, and vinculin as a loading control. The inset at right shows the exposure from a low-bis gel in which the UFD2a-7 isoform of intermediate size is more clearly separated from UFD2a-7/7a at Day 5 and more clearly shows its absence at Day 12 (arrows point to the two isoforms). B). Skeletal muscle (upper panels; pooled gastrocnemius, soleus, and quadriceps muscles) or hearts (lower panels) from E14, E16, and E18 embryos and P1 and P7 pups were dissected from individual embryos or pups at each time point and analyzed by Western blotting for UFD2a (note a second set of mice are shown in Fig S2). Adult mouse heart (H), skeletal muscle (SkM), and spleen (Sp) were simultaneously analyzed for comparison. C). RNA was extracted from whole zebrafish embryos at 10, 12, 24, and 48 hpf, and nested PCR was performed using primers F3 and R3 on the 873- and 756-bp fragments produced from the initial RT-PCR.