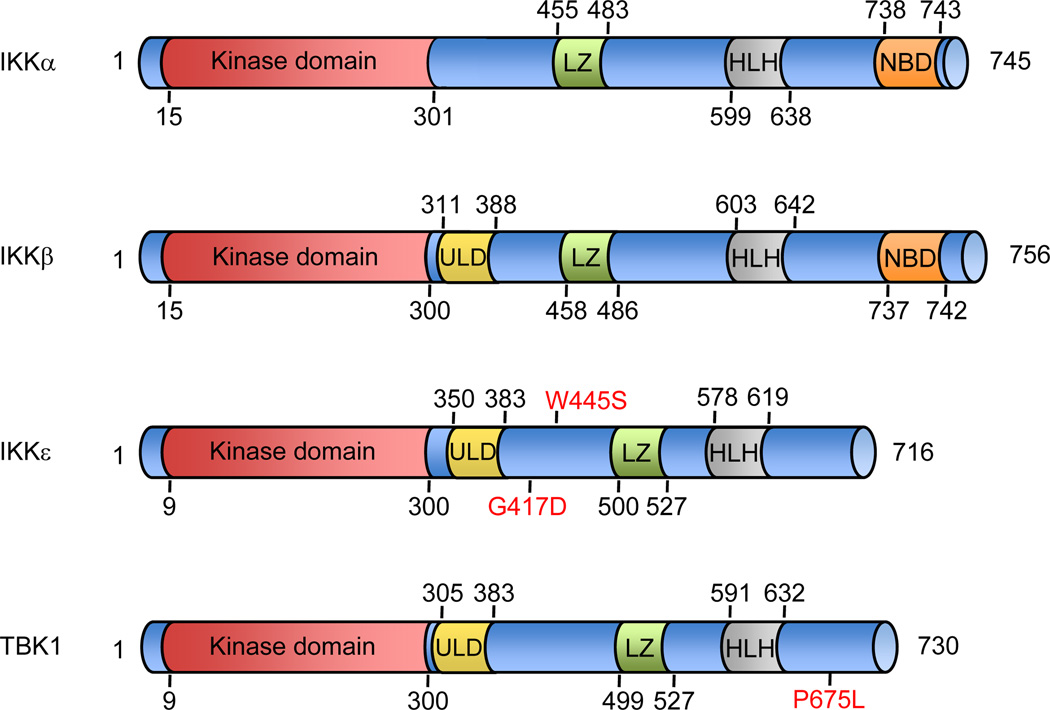
Figure 1. Structural comparison of the classical and non-canonical IKKs.
The major domains of each IKK kinase are depicted with amino-acid numbers that correspond to the human proteins. The kinase domain of IKKε exhibits 27% and 24% identity to IKKα and IKKβ respectively, and TBK1 shares 49% identity and 65% similarity to IKKε. Somatic mutations of IKKε and TBK1 recently identified in lung adenocarcinomas are marked in red. ULD, ubiquitin-like domain; LZ, leucine zipper; HLH, helix-loop-helix; NB, NEMO-binding domain (Hiscott et al., 2006; Kan et al., 2010; May et al., 2004; Perkins, 2007).