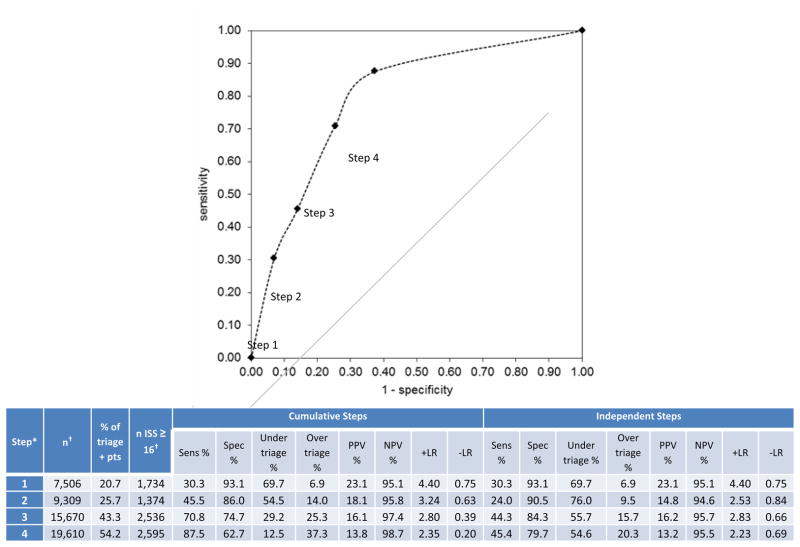
Figure 2.
Diagnostic metrics and receiver operating characteristic curve for identifying major trauma patients (ISS ≥ 16) using each “step” of the Field Triage Decision Scheme among 6 sites (n = 89,441). *Data were restricted to 6 sites, as the 7th site did not collect adequate information necessary to categorize the triage steps. Diagnostic metrics for the “Cumulative Steps” section includes patients from each of the previous incremental steps in the triage algorithm, while metrics for the “Independent Steps” section assesses each of the triage steps independently. There were 36,230 (40.5%) patients in the 6-site sample that met field triage criteria and 5,720 (6.4%) with ISS ≥ 16. The overall ROC value for the Field Triage Decision Scheme using the 6-site sample is 0.75. *Triage steps include: 1 (physiologic), 2 (anatomic), 3 (mechanism of injury) and 4 (special considerations). †The number of patients in each triage step is based on the total number of patients meeting triage criteria for each independent step. As patients can meet criteria from multiple different triage steps, the column totals for number of triage-positive patients and number of patients with ISS ≥ 16 will be greater than the actual number of patients (ie, the triage steps are not mutually exclusive). EMS, emergency medical services; ISS, Injury Severity Score; sens, sensitivity; spec, specificity; CI, confidence interval; PPV, positive predictive value; NPV, negative predictive value; +LR, positive likelihood ratio; −LR, negative likelihood ratio; AUC, area under the curve.