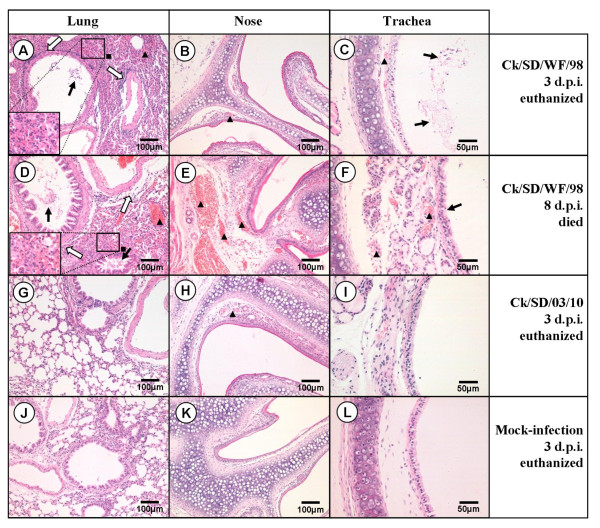
Figure 4.
Representative histopathological changes in Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E)-stained respiratory system tissues (nose, trachea, and lung). Ck/SD/WF/98 virus-infected mice displayed severe bronchopneumonia and interstitial pneumonia in lung tissues (A and D), which showed interstitial edema and thickening of the alveolar walls, alveolar lumen flooded with dropout of alveolar cells, erythrocytes, and inflammatory cells (black square), bronchial epithelial cell desquamation (thick solid arrow) and extensive lymphocyte, neutrophil, and plasma cell infiltrates around the bronchiolitis and blood vessels (thick white arrow); congestion in the blood vessels (black triangle); Light (B, H) and intense (E) congestion in the blood vessels of the nasal submucosa caused by the Ck/SD/WF/98 and Ck/SD/03/10 viruses, respectively (black triangle); Congestion in the blood vessels of the tracheal submucosa (black triangle) and dropout of the mucous epithelium in the trachea (thick solid arrow) caused by the Ck/SD/WF/98 virus (C and F). There were no obvious histopathological changes in the respiratory system tissues of the Ck/SD/03/10-infected group and no significant difference compared to the PBS mock-infection group.