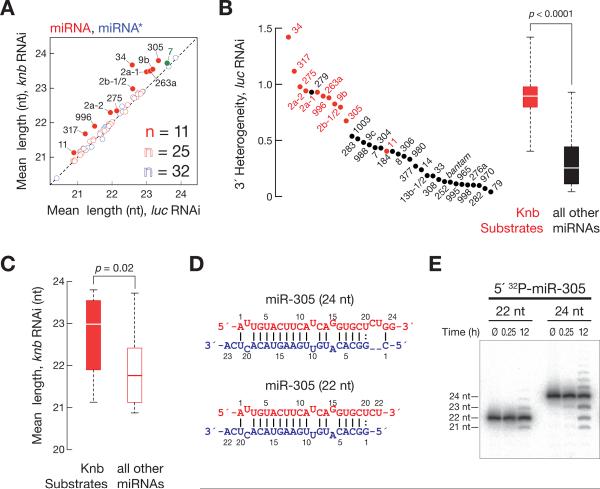
Figure 4. Knabber trims a quarter of all miRNAs in S2 cells.
(A) Analysis of mean miRNA and miRNA* length in S2 cells transfected with dsRNA targeting knabber or a control dsRNA targeting firefly luciferase. miRNA, red; miRNA*, blue; filled circles indicate miRNAs with a significant increase in mean length. In S2 cells, miR-7 (green) does not match our conservative criteria for Knabber substrates, but in flies, miR-7 is trimmed by Knabber (Figure S5C). (B) Knabber trimming explains miRNA 32 heterogeneity. 32 heterogeneity was determined for all S2 cell miRNAs that were more abundant than 200 ppm in high throughput sequencing data. Red, the 11 Knabber substrates identified in this study. Boxplots illustrate 32 heterogeneity of Knabber substrate miRNAs (red) versus all other miRNAs (black). P-value was determined using the Mann-Whitney U test. (C) The mean length of Knabber substrate miRNAs is longer than non-Knabber substrate miRNAs in S2 cells treated with knabber dsRNA. P-value was determined using the Mann-Whitney U test. (D, E) Synthetic miRNA/ miRNA* duplexes comprising a 24 or 22 nt 52 32P-radiolabeled miR-305 RNA and the corresponding miRNA* strand (D) were incubated in embryo lysate, and the products analyzed by denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (E). See also Figure S4 and Tables S1 and 2.