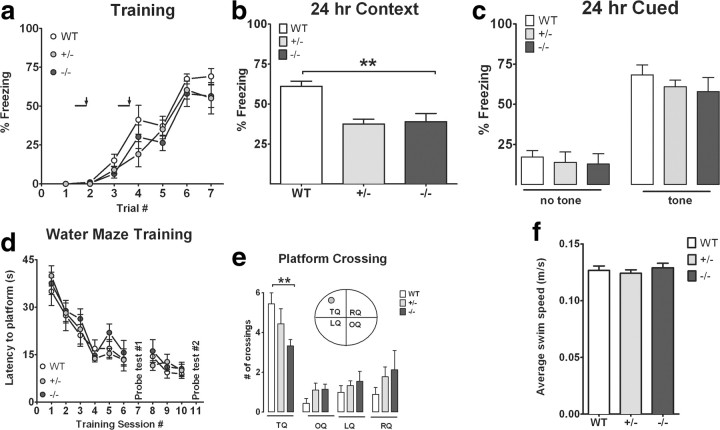
Figure 3.
CX3CR1−/− mice show impairment in contextual fear conditioning and Morris water maze memory function. CX3CR1−/− (black circles) and CX3CR1+/− (gray circles) are compared to littermate wild-type mice (white circles). a, A tone (solid bar) was paired with a foot shock (arrowhead) at 2 and 4 min. Freezing behavior is shown on the day of training for CX3CR1−/−, CX3CR1+/−, and wild-type mice and is comparable in all groups. b, CX3CR1−/− and CX3CR1+/− mice showed significant reduced freezing response compared to wild-type when tested 24 h following training. c, CX3CR1−/− and CX3CR1+/− mice showed normal freezing to cue component compared to controls. **p < 0.01. d, e, The hidden-platform version of the Morris water maze task. d, Mean latency to escape from a pool to hidden platform across training days. e, A first probe test was performed on Day 7, and a second probe test was performed on Day 11 to determine the number of pseudo-platform crossings in the target quadrant (TQ) compared to the opposite quadrant (OP), the left quadrant (LQ), and the right quadrant (RQ). White bar, WT; gray bar, CX3CR1+/−; black bar, CX3CR1−/−. All data are presented as mean ± SEM. p < 0.01. f, Average swim speed. No differences were seen in the overall swim distance between WT, CX3CR1−/− and CX3CR1+/− mice during the probe test.