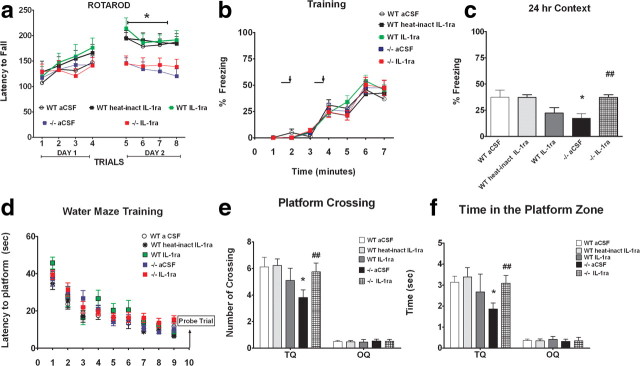
Figure 7.
IL-1ra reversed the deficit in contextual fear conditioning and Morris water maze memory function induced by the loss of CX3CR1 but not the deficit in motor learning. a, CX3CR1−/− ACSF-treated (blue squares) and CX3CR1−/− IL-1ra-treated mice (red squares) are compared to wild-type ACSF-treated mice (open circles), wild-type mice treated with heat-inactivated IL-1ra (black squares), and wild-type mice treated with IL-1ra (green squares). On the first day of training (Trials 1–4), no difference between groups was observed in the learning ability on the rotarod task. On the second day of training (Trials 5–8), all wild-type mouse groups learned the rotarod task as demonstrated by their ability to remain on the rod for longer periods. Neither the CX3CR1−/− ACSF-treated nor CX3CR1−/− IL-1ra-treated mice showed significant improvement in motor coordination with training when compared to wild-type. b, A tone (solid bar) was paired with a foot shock (arrowhead) at 2 and 4 min. Freezing behavior is shown on the day of training for CX3CR1−/− ACSF-treated mice (blue squares), CX3CR1−/− IL-1ra-treated mice (red squares), wild-type ACSF-treated mice (white circles), wild-type treated with heat-inactivated IL-1ra (black squares), and wild-type IL-1ra-treated mice (green squares) and is comparable in all groups. c, CX3CR1−/− control mice showed significantly reduced freezing compared to all wild-type groups when tested 24 h after training. d, CX3CR1−/− treated with IL-1ra (red squares) showed a freezing response similar to that of wild-type groups. d–f, The hidden-platform version of Morris water maze task. Mean latency to escape from a pool to hidden platform across training days (d). A probe test was performed on Day 10 to determine the number of pseudo-platform crossings in the target quadrant (TQ) compared to the opposite quadrant (OP) (e). White bar, WT ACSF-treated mice; light gray bar, wild-type treated with heat-inactivated IL-1ra; dark gray bar, wild-type treated with IL-1ra; black bar, CX3CR1−/− ACSF-treated mice; black/white bar, CX3CR1−/− IL-1ra-treated mice. f shows the time spent in the target platform zone. CX3CR1−/− ACSF-treated mice (black bar) spent significantly less time in the target zone compared to wild-type controls [white bar, wild-type ACSF-treated mice; light gray bar, wild-type heat-inactivated IL-1ra-treated mice; dark gray bar, wild-type IL-1ra-treated mice]. CX3CR1−/− mice treated with IL-1ra spent the same amount of time in the target quadrant compared to wild-type controls. All data are presented as mean ± SEM. p < 0.01. *p < 0.05 (CX3CR1−/− control vs wild-type controls); ##p < 0.001 (CX3CR1−/− IL-1ra vs CX3CR1−/−).