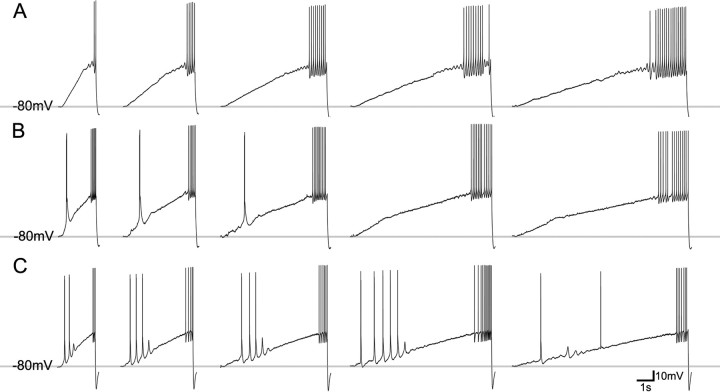
Figure 3.
Three types of neurons are distinguished by their responses to depolarizing current ramps. Current ramps of variable slope (400 pA; durations of 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 s) were injected into neurons that were sufficiently hyperpolarized to de-inactivate T-type calcium channels (−80 mV). The ramps ensured that all cells were sufficiently depolarized to pass the LTS activation window to elicit tonic firing. A, Low burst propensity neuron. Current ramps evoke action potentials but not LTSs (juvenile dLGN neuron shown). B, Medium burst propensity neuron. Steep current ramps evoke a single LTS (juvenile pulvinar neuron shown). C, High burst propensity neuron. Current ramps of variable slope evoke multiple LTSs (adult pulvinar neuron shown).