Figure 6.
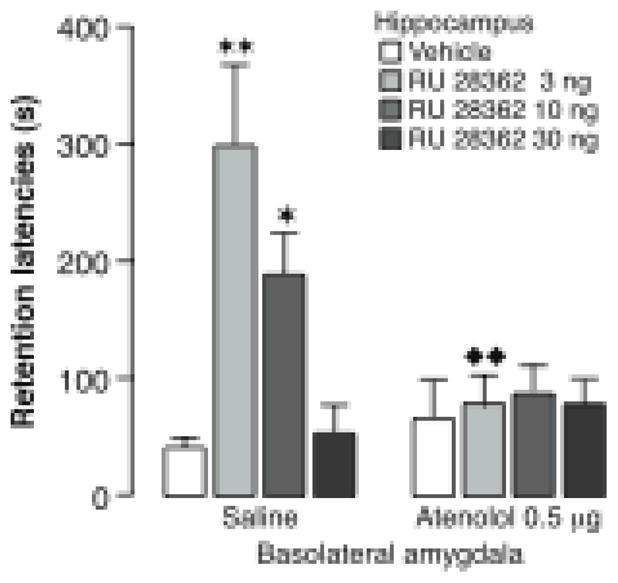
Glucocorticoid effects in the hippocampus on memory consolidation require noradrenergic activity of the basolateral amygdala. Immediate posttraining unilateral infusions of the glucocorticoid receptor agonist RU 28362 (3, 10 or 30 ng in 0.5 μl) into the hippocampus induced dose-dependent enhancement of 48-hour inhibitory avoidance retention latencies in rats given saline infusions into the basolateral amygdala concurrently. Ipsilateral infusions of the β-adrenoceptor antagonist atenolol (0.5 μg in 0.2 μl) into the basolateral amygdala blocked the memory enhancement induced by the glucocorticoid receptor agonist. Results represent retention latencies (mean + SEM) in seconds. ★, P < 0.05; ★ ★, P < 0.01 compared with the corresponding vehicle group. ❶ ❶, P < 0.01 compared with the corresponding saline group. From Roozendaal et al., 1999b.
