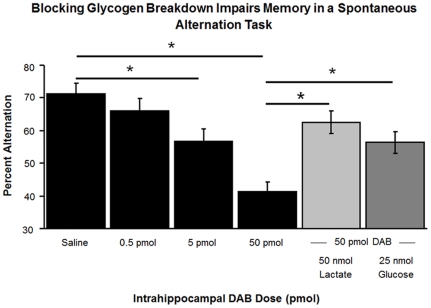
Figure 5. Impairment of memory by DAB injections, used to inhibit glycogenolysis.
The impairment was reversed by lactate or glucose, which can act downstream of glycogenolysis. 1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-D-arabinitol (DAB) injected into the ventral hippocampus 5 min prior to testing significantly impaired scores on a 4-arm spontaneous alternation task (n = 12; Percent Alternation ± SEM: Saline = 71%±3.7% vs. 5 pmol DAB = 58.8%±3.6%, p<0.02 and vs. 50 pmol DAB = 41.6%±3.2%, p<0.001). The performance deficit created by 100 µM of DAB was significantly reversed by the co-administration of 100 mM lactate or 50 mM glucose (Percent Alternation ± SEM: 50 pmol DAB = 41.6%±3.2% vs. 25 nmol of glucose and 50 pmol DAB = 62.6%±3.1%, p<0.001 and 50 nmol of lactate and 50 pmol DAB = 56.2%±2.9%, p<0.01).