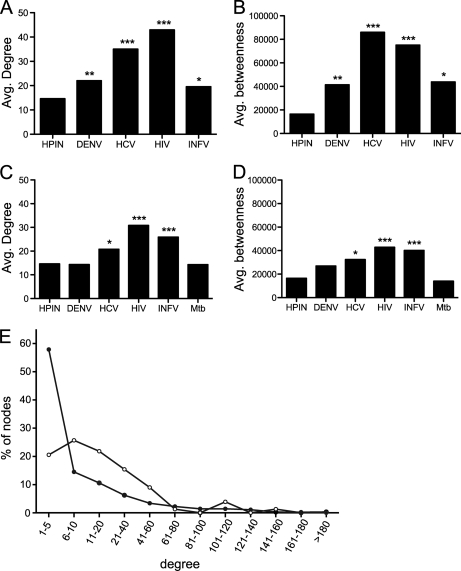
Fig. 6.
Elevated degree and betweenness in cellular proteins implicated in virus infection. A, average degree (k) of human proteins that bound to viral proteins from DENV (this study), HCV, HIV, and INFV. B, Average betweenness centrality (b) of human proteins that bound to viral proteins from DENV (this study), HCV, HIV, and INFV. C, average degree (k) of human proteins that were identified in siRNA screens for cellular cofactors of DENV, HCV, HIV, INFV, and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. D, average betweenness centrality (b) of human proteins that were identified in siRNA screens for cellular cofactors of DENV, HCV, HIV, INFV, and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Average degree and betweenness centrality were calculated for each data set and compared with the same values from a randomly chosen set of human proteins of the same size. Asterisks indicate statistical significance. * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.001, *** p ≤ 1 × 106. E, degree distribution of human proteins in the DENV-human protein interaction network (open circles) and the human-human protein interaction network (closed circles). Proteins were binned according to the number of binding partners as indicated.