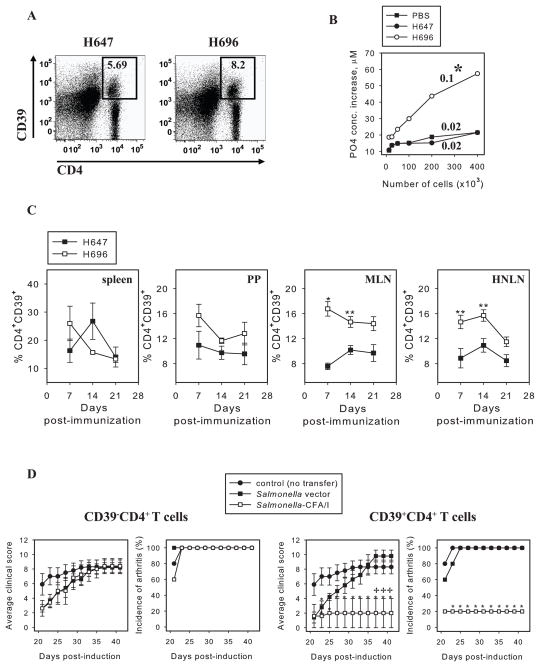
FIGURE 3.
Salmonella-CFA/I stimulates CD39+CD4+ T cells protective against CIA. FoxP3-GFP Tg mice were immunized with Salmonella-CFA/I (H696) or Salmonella vector (H647), and on day 14 post-immunization, flow cytometry analysis was performed on stained lymphocytes of individual mice (5 mice per group). A, Representative FACS plots of CD39 expression by MLN CD4+ T cells out of total lymphocytes gated. B, Extracellular ATP hydrolysis by CD4+ T cells on day 14 post-immunization of mice with Salmonella-CFA/I, Salmonella vector, or PBS. ATP consumption was evaluated as an increase in PO43− concentrations relative to control reaction lacking exogenous ATP (base line hydrolysis). ATPase activity is calculated as fmoles of phosphate/sec per cell. Numbers above the curves represent ATPase activity. One of 4 experiments is depicted; p = 0.026. C, CD39 expression kinetics by CD4+ T cells in spleen, PPs, MLNs, and HNLNs of individual C57BL/6 mice (3/time point) after immunization with Salmonella-CFA/I or Salmonella vector. *p < 0.005; **p < 0.05. D, Adoptive transfer of Salmonella-CFA/I-induced CD39+, not CD39− CD4+, T cells protects against CIA. On day 0, arthritis was induced in recipient mice, and donor mice were immunized with Salmonella-CFA/I or Salmonella vector. On day 14 post-immunization, CD39+CD4+ and CD39− CD4+ T cells were sorted from immunized C57BL/6 donors and adoptively transferred to CIA recipients (5 mice per group). *p<0.05 versus PBS-treated group; +p < 0.05 versus recipients of Salmonella vector-induced cells.