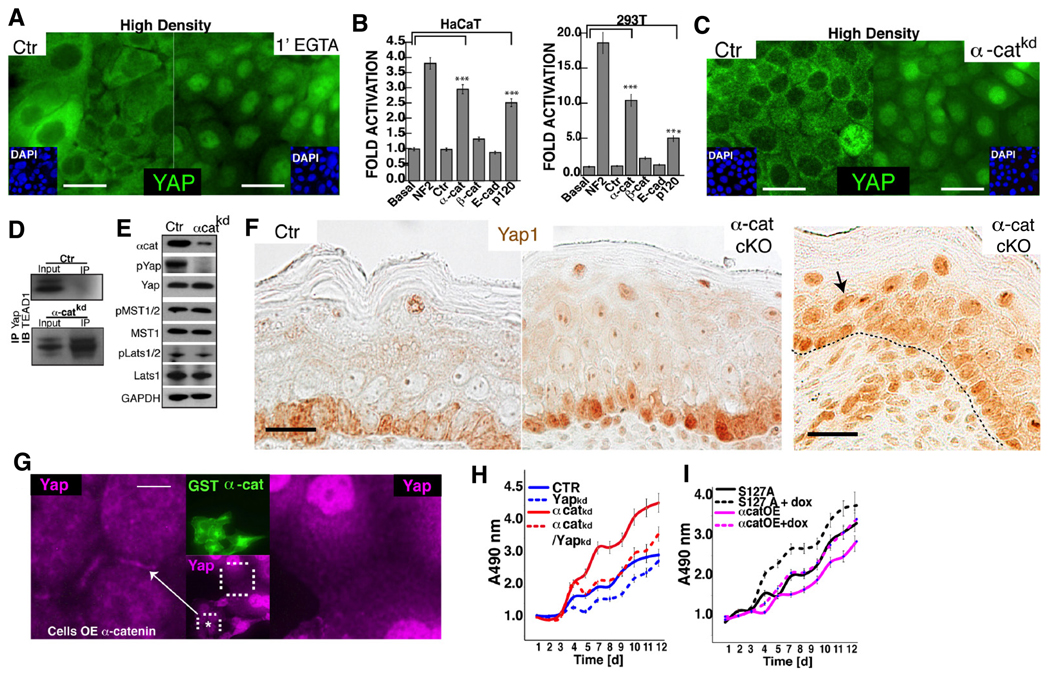
Figure 6. α-Catenin regulates Yap1 localization and activity.
A, Disruption of AJs in high-confluent keratinocytes with EGTA results in Yap1 nuclear localization after 1-minute of treatment. B, Knockdown (KD) of AJ proteins in either HaCaT or 293T cells carrying the TBS-reporter. KD of NF2 is shown as a positive control. C, KD of α-cat in confluent keratinocytes leads to Yap1 nuclear localization, and interaction with its nuclear partner Tead1 (D). E, siRNA-mediated depletion of α-cat in high density HaCaT cultures leads to loss of Yap phosporylation at serine 127 (pYap), and unchanged levels of activated Mst1/2 (pMst) or Lats1/2 (pLats). F, Immunohistochemistry for Yap1 in Ctrl and K14-Cre conditional α-catenin mutant (cKO) E18.5 epidermis. Note enhanced nuclear staining in basal and suprabasal cells of cKO mice. G, Immunofluorescence detection of Yap1 (purple) localization in low-density keratinocytes ectopically expressing GST-α-cat (green). Keratinocytes overexpressing α-cat show Yap1 localization to sites of cell-cell contact, whereas untransfected cells show nuclear staining and an absence of Yap1 staining at the cell membrane. H, Stable-knockdown of α-catenin (α-cat-KD) promotes hyperproliferation in HaCaT cells, however doxycycline (dox)-induced KD of Yap1 in α-cat-KD cells slows down the rate of cell proliferation to control (Ctr) levels. I, Ectopic expression of α-cat in a HaCaT cells suppresses cell proliferation (α-catOE). This growth inhibition is rescued by the expression of a Dox-inducible Yap1S127A mutant (Yap1S127A+Dox). Data are mean ± standard deviation (error bars), ***p < 0.001. Scale bars are 20 µm (A, C), and 10 µm (F), 5 µm (G). See also Supplementary Figure S5C–H and S6A–E.