Fig. 3.
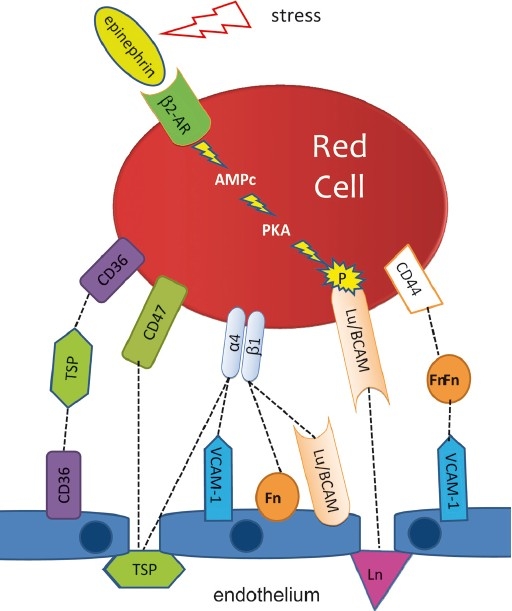
Adhesion of sickle red blood cells to the endothelium and cell activation. Simplified scheme of the main interactions involved in the abnormal adhesion of the sickle red blood cells to the endothelium. Locally, endothelial damage exposes sub-endothelial structures that also participate to the adhesion process. Some adhesion proteins are activated by extracellular stimuli. It is the case of the basal cell adhesion molecule (Lutheran blood group) (Lu/BCAM) that expresses its adhesion properties only when phosphorylated via the protein kinase A-dependent (PKA) pathway when the red blood cell is activated by epinephrine. 2-AR, type 2 adrenergic receptor; Fn, fibronectin; TSP, thrombospondin; Ln, laminin; α4β1, α4β1 integrin (or VLA-4). [Source: Modified from Elion et al34].
