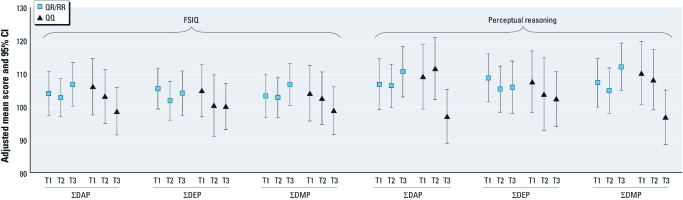
Figure 1.
Multivariate adjusted mean estimates and 95% CIs according to tertiles (T) of exposure and PON1 Q192R genotype. Among the children of mothers with the PON1 192QQ genotype (triangles), increasing tertile of ΣDAP, ΣDEP, and ΣDMP exposure was generally associated with a monotonic decline in the combined WISC-IV/WPPSI-III FSIQ and Perceptual Reasoning domains, adjusted for sex, race/ethnicity, maternal education, language in the home, alcohol use in pregnancy, batch and season of urine collection, urinary creatinine, and an indicator variable to designate the WISC-IV or WPPSI-III instrument. We found no consistent patterns in the QR/RR genotype group (squares). There was considerable imprecision in all estimates. The first- versus third-tertile contrasts for Perceptual Reasoning were significantly different at p < 0.05 for ΣDAP and ΣDMP.