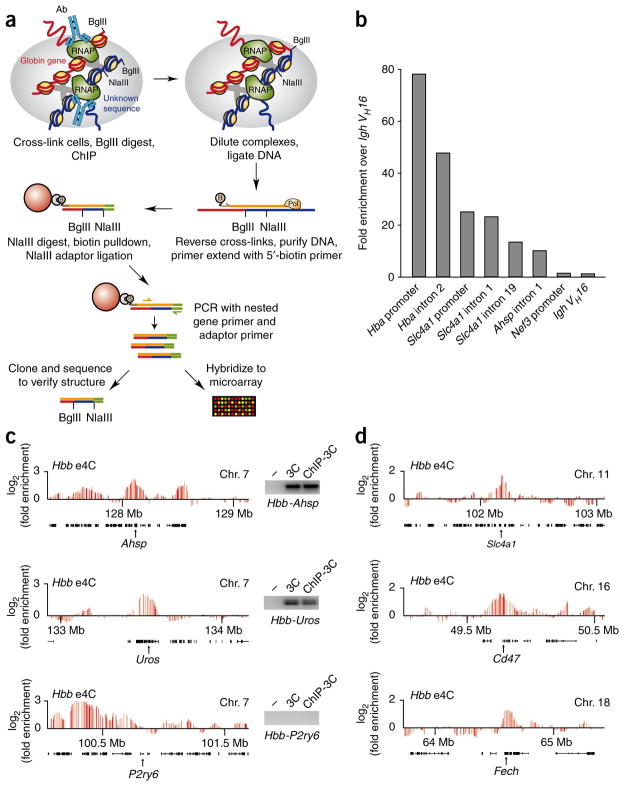
Figure 2.
e4C detects known and heretofore uncharacterized genomic co-associations with Hbb in cis and trans. (a) Overview of the e4C method. Nuclei are cross-linked, and the chromatin is digested with BglII as in conventional 3C, before immunoprecipitation with an antibody recognizing RNAPII-S5P. DNA ligation is performed on the immunoprecipitated chromatin under dilute conditions that favor ligation between DNA strands within cross-linked complexes. After reversal of the cross-links and DNA purification, a biotinylated primer (brown) specific to the bait gene (red) is used for primer extension into adjacent ligation products (blue). Biotinylated extension products are purified on streptavidin-coated magnetic beads (red sphere), digested with NlaIII and ligated to an adaptor (green). e4C products are amplified by PCR with a nested, bait-specific primer (yellow) and an adaptor-specific primer (green). e4C products are then analyzed by cloning and sequencing, or hybridization to a custom microarray. (b) Bar chart showing the enrichments of erythroid-expressed Hba, Slc4a1 and Ahsp sequences after ChIP using an antibody recognizing RNAPII-S5P. Enrichments of nonexpressed Nefm (formerly Nef3) and Igh VH16 sequences are shown as negative controls. Enrichments are shown relative to the VH16 control. (c) Hbb e4C microarray profiles for three ~2-Mb regions of genomic sequence in cis to Hbb, centered on Ahsp, Uros and P2ry6, showing the running mean enrichments of e4C signal over genomic signal for 100-kilobase (kb) windows. Black bars denote the positions of genes within these regions. Insets show PCR products for ligation products between Hbb and Ahsp, Uros or P2ry6 on water (−), 3C or RNAPII-S5P ChIP-3C templates. (d) Hbb e4C microarray profiles for three ~2 Mb regions of genomic sequence in trans to Hbb, centered on Slc4a1, Cd47 and Fech, showing the running mean enrichments of e4C signal over genomic signal for 100-kb windows.