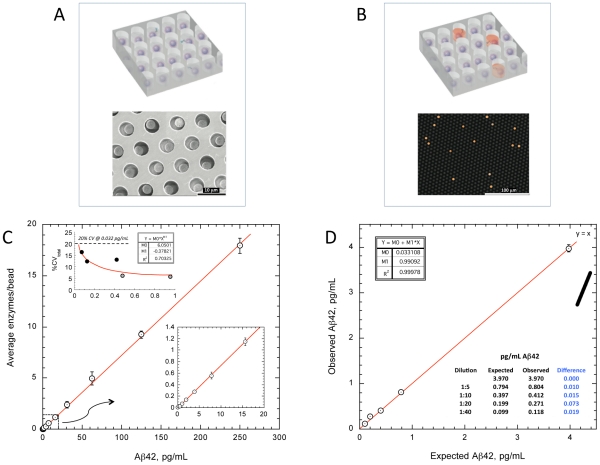
Figure 1. Assay characteristics.
Arrays of femtoliter-volume wells permit isolation of 2.7 mm capture beads from a standard bead-based ELISA (A), enabling exquisite sensitivity to enzyme label by preventing fluorescent product from diffusing away into a bulk solution. At very low concentrations of Aβ42, beads contain either a single labeled immunocomplex or no complexes, giving rise to digital signal output corresponding to single molecules (B). Simultaneous counting of active wells across an array statistically powers estimates of average enzymes/bead. (C) Dose-response of digital immunoassay for Aβ42 (n = 3). Y-axis refers to average number of enzyme labels per individual microbead captured in the array. The concentration of label is reduced relative to standard immunoassays, resulting in improved signal∶background at very low Aβ42 concentration. Assay calibrators were purified Aβ42 (Merck) in PBS/BSA. (C inset) Limit of quantification (LoQ) was estimated from total coefficients of variation (CV) from five low panel members (spiked PBS/BSA panels, grey circles, and immunodepleted plasma, black circles) assayed repeatedly across five days. The Aβ42 concentration at which total assay imprecision reached 20% (LoQ) was 0.032 pg/mL. (D) Recovery at extremely low Aβ42 concentrations was tested by diluting spiked immunodepleted plasma with PBS/BSA zero calibrator (n = 3). Because samples are pre-diluted 4-fold prior to assay to reduce matrix effects, dilutions include an initial 4-fold dilution.