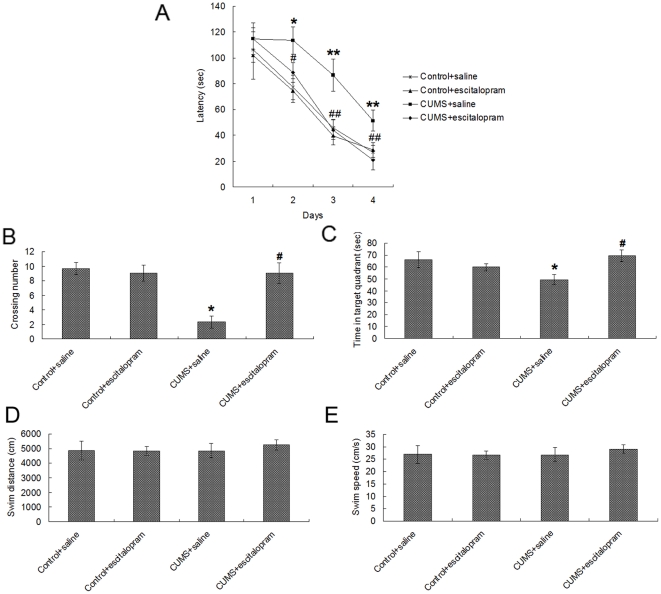
Figure 2. Effects of CUMS and escitalopram treatment on acquisition and consolidation in the Morris water maze test.
(A) In the acquisition trials, CUMS rats showed longer escape latency during training days 2–4, while escitalopram treatment restored the CUMS-induced longer latencies to control levels. In the probe trial, CUMS impaired memory retrieval as indicated by fewer crossing times of the platform position (B) and less time spent in the target quadrant (C), while escitalopram treatment restored the CUMS-induced impairment of memory retrieval to levels seen in controls. There was no significant difference of swim distance (D) and swim speed (E) among groups. Data are presented as mean ± S.D. (n = 6 per group). * P<0.05, ** P<0.01 vs. control+saline group. # P<0.05, # # P<0.01, vs. CUMS+saline group.