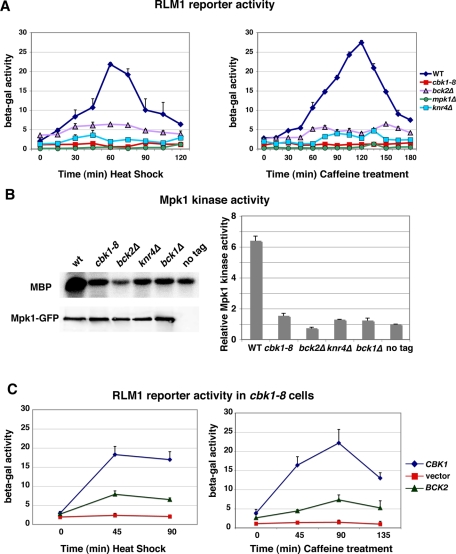
FIGURE 2:
Cbk1 and Bck2 are required for Mpk1 kinase activity and Rlm1 reporter activation. (A) An RLM1-lacZ reporter plasmid was introduced into yeast cells, and reporter activity was measured at the designated time points following heat shock (left) or caffeine treatment (right). Rlm1-dependent lacZ expression was quantified as nanomoles per minute per milligram of o-nitrophenyl phosphate produced from o-nitrophenyl β-d-galactoside substrate. (B) In vitro kinase assays were performed with immunoprecipitated Mpk1-GFP and myelin basic protein (MBP) as substrate. Top, an autoradiogram of phosphorylated MBP; bottom, an immunoblot of immunoprecipitated Mpk1 (probed with anti-GFP) from wild-type (WT), cbk1-8, bck2Δ, knr4Δ, bck1Δ, and untagged wild-type cells (lacking Mpk1-GFP). The graph shows the relative phosphorylated MBP levels quantified from two independent experiments. The relative MBP phosphorylation levels were normalized to the negative control (untagged cells). (C) Bck2 overexpression via high-copy pGP564-BCK2 partially restores the Rlm1 reporter activity in heat -shocked (left) and caffeine-treated (right) cbk1-8 cells. Parallel experiments were done with pCBK1 (YGPM11e20) and empty vector (pGP564) for positive and negative controls. The yeast strains used in these experiments were FLY1300, FLY2884, FLY3270, FLY3271, FLY3276, and FLY3277.