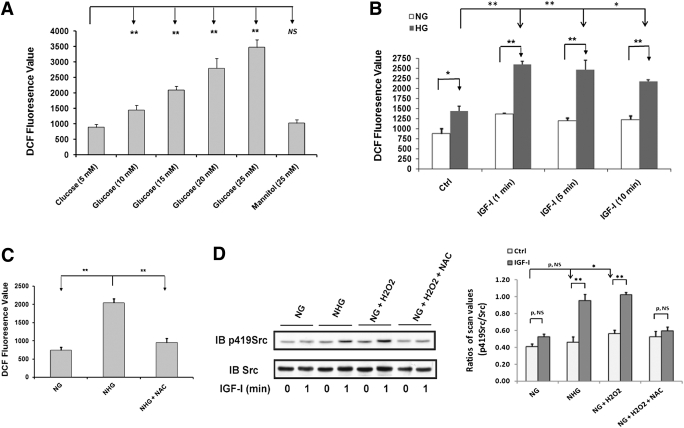
FIG. 2.
Hyperglycemia- and IGF-I–induced ROS are required for Src activation in response to IGF-I during hyperglycemia. A: VSMCs were cultured in DMEM containing normal glucose (NG; 5 mmol/L) and serum starved for 16 h before addition of the indicated glucose concentration. Mannitol (25 mmol/L) was used as an osmotic control. B: VSMCs were cultured in DMEM containing high glucose (HG; 25 mmol/L) or NG (5 mmol/L) and serum starved for 16 h before addition of IGF-I (100 ng/mL) for the indicated times. C: Cells were cultured in DMEM containing NG plus 10% FBS and serum deprived for 16 h with DMEM containing NG or HG (NHG) before ROS measurement. NAC was added with serum-free DMEM and incubated for 16 h. ROS generation was determined according to the procedure described in research design and methods. D: Cells were cultured in DMEM containing NG plus 10% FBS and serum deprived for 16 h in DMEM containing NG or HG (NHG). For NAC treatment, 2 mmol/L NAC was added and incubated for 16 h before IGF-I treatment. H2O2 (200 μmol/L) was added for 1 h before IGF-I exposure for the indicated times. Cell lysates were immunoblotted with an anti-p419Src antibody and reprobed with an anti-Src antibody as a loading control. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 indicate significant differences between two treatments. The figures are representative of three independent experiments.