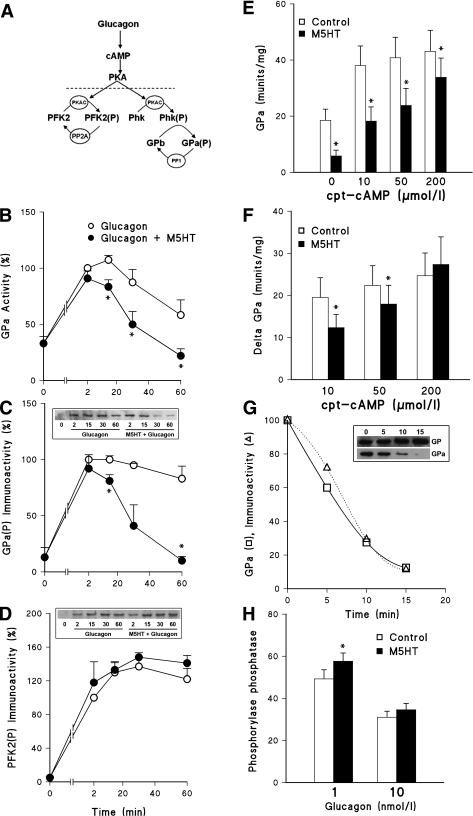
FIG. 4.
Methyl-5HT (M5HT) inactivates glycogen phosphorylase by a mechanism downstream of PKA. A: Glucagon activates PKA, causing phosphorylation of PFK2 (Ser32) and Phk, which phosphorylates GPb to GPa. Time course of the effect of glucagon (10 nmol/L) without (○) or with (●) 100 μmol/L methyl-5HT on GPa enzyme activity (B), GPa(P) immunoactivity (C), and PFK2-Ser32(P) immunoactivity (D); n = 4. Results expressed as % of glucagon 2 min. *P < 0.05 effect of methyl-5HT. E and F: Hepatocytes were incubated for 1 h with the concentrations of cpt-cAMP indicated without or with 100 μmol/L methyl-5HT (M5HT). E: GPa activity at the end of incubation. F: Increment in GPa activity caused by cpt-cAMP above corresponding control; n = 4. *P < 0.05 effect of methyl-5HT. G and H: Hepatocytes were incubated with methyl-5HT (100 μmol/L for 5 min) followed by glucagon (1 or 10 nmol/L for 60 s), and phosphorylase phosphatase (PP) activity was determined as described in the research design and methods. G: Representative time course of phosphorylase phosphatase activity determined from the decline in GPa activity (□) and GPa(P) immunoactivity (△) showing immunoblot for GPa(P) and total glycogen phosphorylase (GP). H: Phosphorylase phosphatase activity (% GPa depletion) after 10 min; n = 6. *P < 0.05 effect of methyl-5HT.