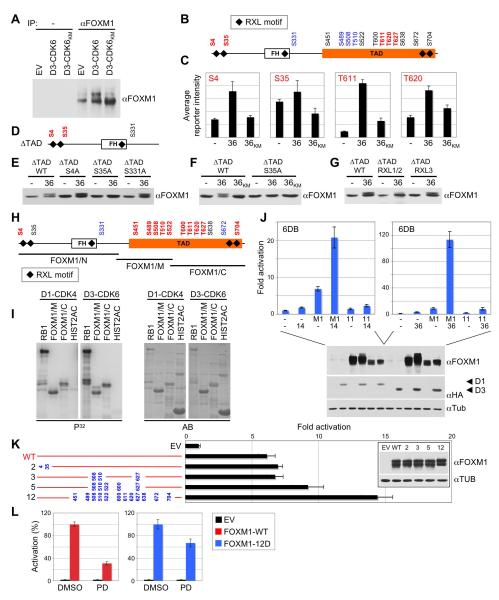
Figure 4. CDK4/6 Activate FOXM1 by Multisite Phosphorylation.
(A) Immunoprecipitation (IP) of endogenous FOXM1 from U2OS cells expressing either empty vector (EV), cyclin D3-CDK6, or cyclin D3 and kinase-inactive CDK6 (CDK6KM).
(B and C) FOXM1 was co-expressed with either empty vector (−), or cyclin D3 and CDK6 (36), or cyclin D3 and kinase-inactive CDK6KM (36KM) in HeLa cells, immunoprecipitated and subjected to quantitative mass spectrometry. In vivo phosphorylated sites are depicted in red; black sites were not accessible to analysis; no phosphorylation was detected on blue sites. Site-specific in vivo phosphorylation quantification (+/−SD) is shown in C.
(D) FOXM1 TAD deletion mutant (ΔTAD) with N-terminal CDK4/6 sites (red).
(E) HeLa cells were co-transfected with either empty vector (−), or cyclin D3 and CDK6 (36), plus FOXM1ΔTAD wild-type (WT) or phosphorylation-site mutants (S4A, S35A, S331A).
(F) FOXM1ΔTAD co-transfections with either empty vector (−), or cyclin D3 and CDK6 (36), or cyclin D3 and kinase-inactive CDK6KM (36KM).
(G) Co-transfections with either empty vector (−), or cyclin D3 and CDK6 (36), and FOXM1ΔTAD wild-type (WT) or RXL mutant versions, in which the RXL motif was replaced by AXA.
(H) FOXM1 fragments (black bars) were in vitro phosphorylated by cyclin D3-CDK6 and analyzed by mass spectrometry. Phosphorylated residues are depicted in red; unphosphorylated sites are blue; black sites were not accessible to analysis.
(I) In vitro phosphorylation assay performed using recombinant cyclin D1-CDK4 or cyclin D3-CDK6 with RB1, FOXM1 middle (M) or C-terminal fragment (C), and histone H2A. P32, autoradiogram; AB, Amidoblack protein staining for total protein amounts.
(J) Activation of the 6DB promoter (+/−SD) by wild-type FOXM1 (M1) versus the ‘11A’ CDK site to alanine mutant plus cyclin D1-CDK4 (14, left panel) or cyclin D3-CDK6 (36, right panel). Protein expression is shown (lower panel).
(K) Effect of phosphomimetic mutations on FOXM1 transcriptional activity (+/−SD). Hela cells were transfected with the 6DB promoter and either empty vector (EV), wild-type FOXM1 (WT), or phosphomimetic mutants (S/T residue numbers replaced by aspartic acid, blue). Expression of the mutant proteins is shown in the inlet.
(L) U2OS cells transfected with the 6DB promoter and either empty vector (EV), wild-type FOXM1 (WT) or the FOXM1 ‘12D’ mutant (12D) were treated with DMSO or 1μM PD0332991 (PD) for 16 h. Values are mean +/−SD. See also Figure S2.