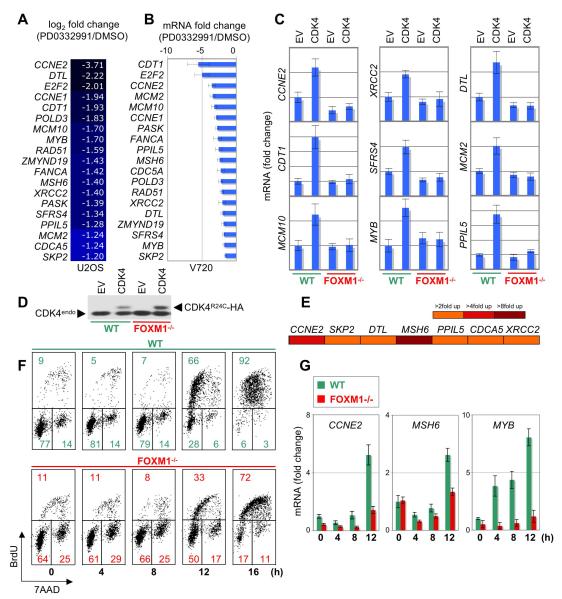
Figure 7. FOXM1 Activates Key G1/S Genes Downstream of CDK4 Function and Promotes G1/S Transition.
(A and B) 19 ‘common’ cyclin D-CDK4/6-regulated genes obtained by microarray analysis from U2OS cells (A), and QPCR analysis (+/−SD) from V720 mouse mammary tumor cells (B). Each cell line was treated with either DMSO or PD0332991 for 4 h. For each cell line, genes are arranged from the highest to lowest change in expression.
(C) QPCR analysis of the indicated genes in wild-type (WT) and FOXM1-/- MEFs, each stably expressing either pBABE empty vector (EV) or CDK4R24C (CDK4). Values derived from WT-EV cells were set to 1-fold change in expression. Values are mean +/−SD.
(D) Protein expression of HA-tagged CDK4R24C and endogenous CDK4 (CDK4endo) in wild-type (WT) and FOXM1-/- MEFs.
(E) U2OS cells were transfected with the indicated promoter-luciferase constructs plus either empty vector or FOXM1. Reporter assay results are visualized as a heat map (scale, right panel).
(F and G) Wild-type (WT) and FOXM1-/- MEFs were serum starved for 48 h, followed by serum addition at the indicated time points. Cell cycle parameters (F) and mRNA expression (G) were subsequently assessed by FACS and QPCR analysis (+/−SD), respectively. See also Figure S5.