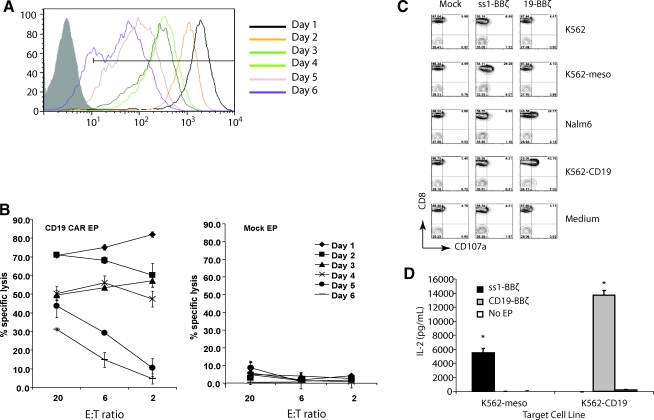
FIG. 1.
Optimized mRNA electroporation procedure results in uniform high-level surface expression and specific function of CAR T cells in vitro. (A) CAR expression as measured by mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) at different time points after electroporation with CD19-BBz mRNA in anti-CD3 and CD28 stimulated peripheral blood T cells (open histograms). Nonelectroporated T cells were used as negative control (filled histogram). (B) RNA CAR+ T cells specifically kill CD19 targets. A flow-based CTL assay was conducted on the indicated day post electroporation with K562-CD19 as target and K562-meso as control (data not shown). (C) Peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBLs) were electroporated with ss1-BBz, CD19-BBz, or no mRNA (Mock). Four hours post electroporation, the T cells were cocultured with K562, NALM-6, or K562 expressing either CD19 (K562-CD19) or mesothelin (K562-meso) and analyzed for CD107a staining. CD3+ T cells were gated. Only antigen-specific CD107a expression is observed. (D) Four hours post electroporation, T cells electroporated with mRNA encoding for CD19-BBz or ss1-BBz were cocultured with K562-meso or K562-CD19 target cells for 16 hr. IL-2 production was measured in the supernatant by ELISA, with significant increases in IL-2 production in an antigen-specific manner (*p<0.01). Data are representative of at least two independent experiments.