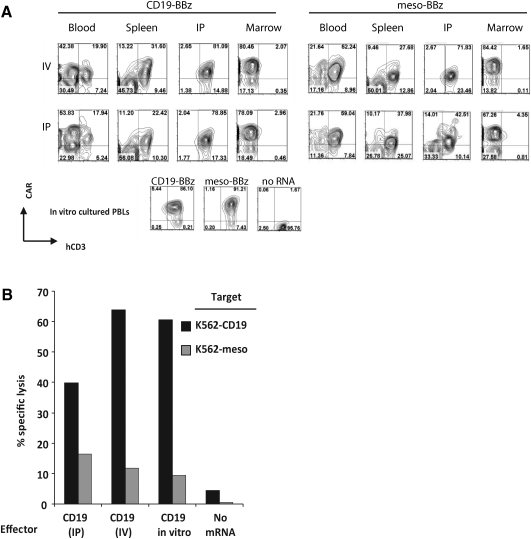
FIG. 3.
Expression and function of RNA CARs in vivo. (A) NOD/SCID/γc–/– null (NSG) mice were injected with 107 PBLs either intravenously (IV) or intraperitoneally (IP) 4 hr after electroporation with ss1-BBz or CD19-BBz. Mice were sacrificed after 48 hr, and human PBLs were isolated from peripheral blood, spleen, bone marrow, and intraperitoneal washing (IP) by using a T cell negative selection kit (Dynal Magnetic Beads). The purified cells were stained for human CD3 and CAR expression (via a panspecific goat anti-mouse IgG) and analyzed by flow cytometry. Significant background staining of mouse marrow precursor cells is observed in the bone-marrow compartment despite negative selection. CD3+CAR+ cells are recovered from blood, spleen, and a peritoneal washing, but rarely from the femoral bone marrow at this time point. (B) Purified T cells recovered from intraperitoneal washings 2 days after injection of mice by the IV or IP route with CD19-BBz were used in a flow-based CTL assay. CD19-BBz RNA electroporated T cells that had been cultured in vitro for 2 days (CD19 in vitro) and mock electroporated T cells (No mRNA) were used as controls. The graph shows percent lysis of the purified PBLs against K562-CD19 or K562-meso targets. Target-specific lysis observed in recovered CAR CTLs is comparable to that of in vitro cultured CAR+ PBLs and is significantly higher than no mRNA controls (p<0.01).