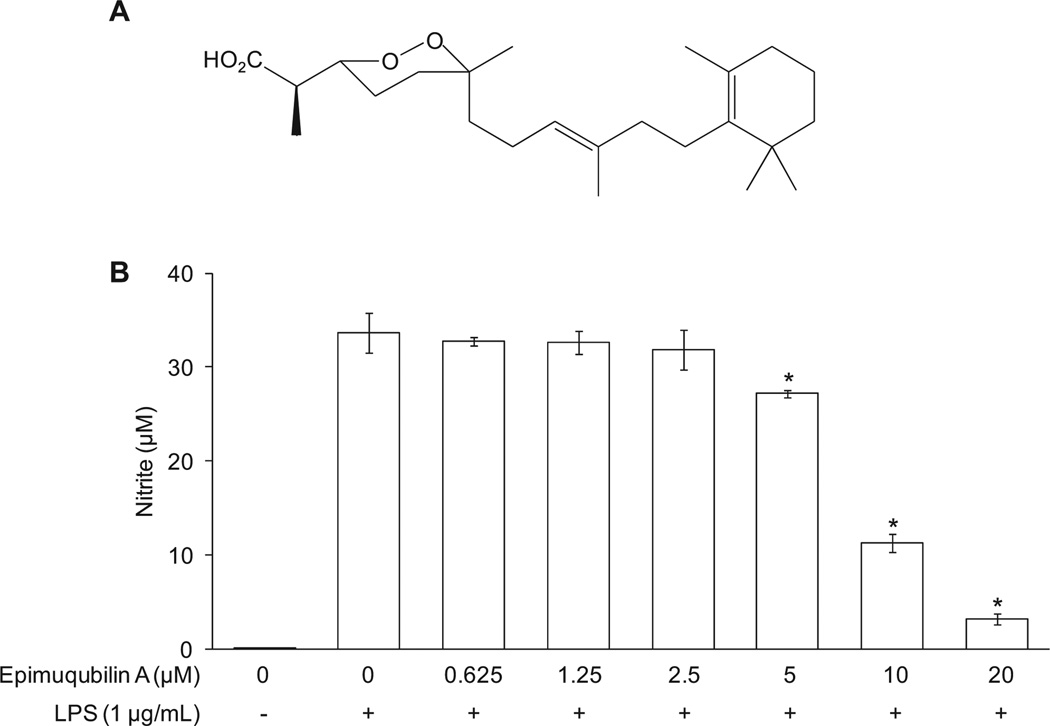
Fig. 1.
Concentration-dependent inhibitory effects of epimuqubilin A on LPS-induced NO production in RAW 264.7 cells. (A) Chemical structure of epimuqubilin A. (B) Cells were pretreated with the indicated concentrations (0–20 µM) of epimuqubilin A for 15 min, and then stimulated with LPS for 20 h. The level of nitrite produced by LPS treatment was significantly suppressed by each concentration of epimuqubilin A. An asterisk (*) indicates a significant difference between the respective groups with P values less than 0.05.