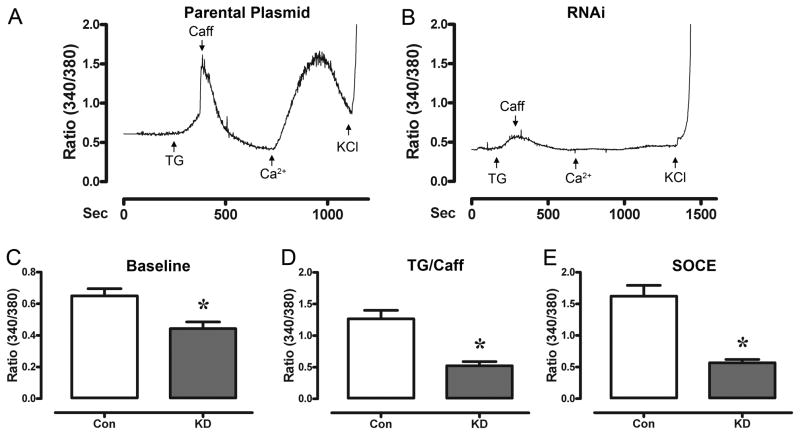
Figure 4. SOCE is abolished following Orai1 knockdown (KD).
Panel A, shows a raw tracing of the ratiometric fluorescent measurements of a HL-1 cell transfected with the parental plasmid (48 hr) during testing for SOCE. Treatment of cells with TG (10 μM, in 0mM Ca2+) created a large accumulation of Ca2+in the cells. Following a return to baseline, the cells were perfused with Ca2+ (1.8 mM), resulting in SOCE. Panel B, a raw tracing of the ratiometric fluorescent measurements of a HL-1 cell targeted for Orai1 KD (48 hr) during testing for SOCE. Note that SOCE is inhibited. Panel C, shows the average ratiometric fluorescence at baseline. HL-1 cells targeted for Orai1 knockdown had lower baseline levels of Ca2+ (n=6 experiments) when compared to control (parental plasmid). Panel D, shows the average ratiometric fluorescence following treatment with TG and Caff. The basal Ca2+ levels and SR-stimulated release of Ca2+ were significantly inhibited in HL-1 cardiomyoctes targeted for Orai1 KD. Panel E, shows the average ratiometric fluorescence following treatment with TG and reperfusion with Ca2+ in HL-1 cells targeted for Orai1 knockdown. n=6 experiments; * indicates significant reduction from control (parental plasmid).