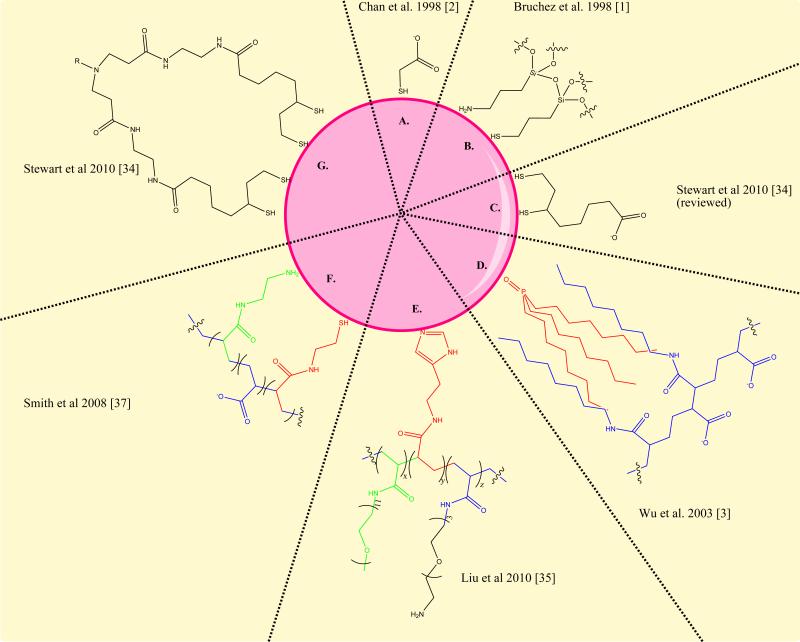
Figure 2. Variations of QD surface chemistry.
Over the past thirteen years, quantum dot surface chemistry has progressed substantially. Some of the initial coatings (A, B, C) were of limited stability and reproducibility. The amphiphilic polymer stabilization (D) developed in 2002, was implemented in the commercially available materials from Invitrogen. More recent chemistries developed to improve the stability and size of quantum dots use multiple attachment groups in RAFT synthesized polymers (E), modified polyacrylic acid (F) or discrete multivalent ligands (G). These final 3 alternatives result in a roughly 50% decrease in the overall hydrodynamic diameter of the aqueous quantum dots.