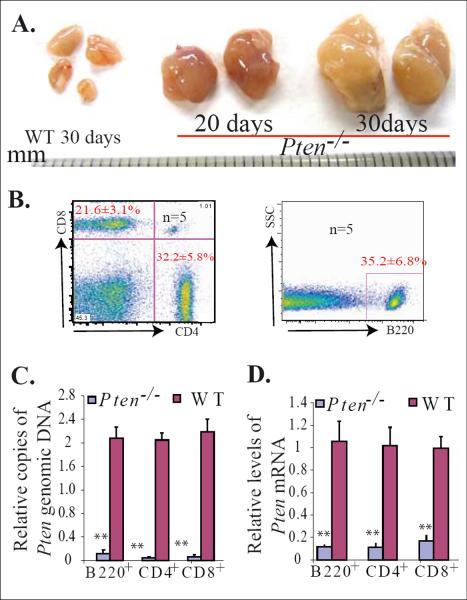
Figure 1.
Early development of lymphadenopathy in inducible Pten−/− mice. Mx1Cre+Ptenfx/fx mice and their littermate Mx1Cre−Ptenfx/fx controls (WT) were injected with polyI:C at age 3 weeks, once every other day for a total of five injections. Lymph nodes were collected 20 or 30 days after the last polyI:C injection. A. Significantly enlarged lymph nodes observed in Pten−/− mice. B. The enlarged lymph nodes contain a mixture of T (CD4+ or CD8+) and B (B220+) lymphocytes, as shown by flow cytometric analysis. C & D. Pten deletion in T and B lymphocytes isolated from enlarged lymph nodes was confirmed by q-PCR and qRT (reverse transcription)-PCR to detect Pten genomic DNA (C) and Pten mRNA levels (D), respectively. T and B lymphocytes isolated from lymph nodes of WT mice (Mx1Cre−Ptenfx/fx) were used as controls. The levels of Pten genomic DNA and mRNA in Pten−/− cells were normalized to levels of Pten genomic DNA and mRNA of their WT counterparts. Triplicate experiments were performed. ** indicates statistical significance compared to WT mice.