Fig. 3.
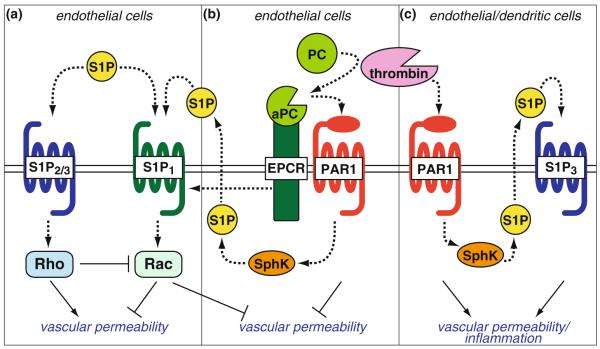
Regulation of vascular permeability by S1P and crosstalk with PAR1 signaling. a In endothelial cells, S1P1 induces Rac-mediated formation of cortical actin and adherens junctions and decreases vascular permeability, whereas S1P2 and S1P3 induce Rho-mediated increases in vascular permeability. b PAR1, when activated by the complex of endothelial protein C receptor (EPCR) and activated protein C (aPC), potently inhibits thrombin-induced vascular permeability. This barrier-protective activity of aPC is partly dependent on cross-activation of S1P1 either by SphK1-mediated S1P production or by EPCR-mediated trans-activation of S1P1. c Thrombin-activated PAR1 increases vascular permeability partly via trans-activation of S1P3. PAR1-S1P3 coupling in dendritic cells leads to the systemic inflammation in the late stage of severe sepsis