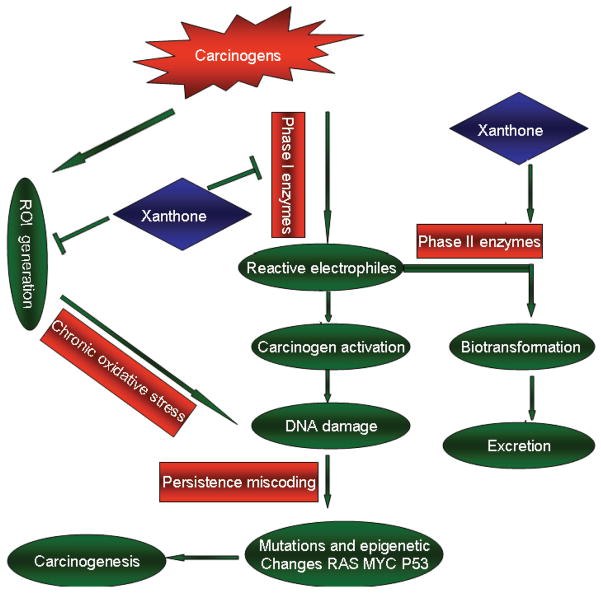
Fig. 3.
Anti-carcinogenesis effects: xanthones modulate carcinogen detoxification mechanism. Many pollutants such as cigarette smoke, industrial emissions, and gasoline vapors can be converted to active carcinogens and produce excessive amounts of reactive oxygen intermediates (ROI). These mediators could cause DNA damage, genomic instability, and carcinogenesis. Xanthones can prevent the malignant conversion of precancerous cells by impacting phase I and phase II enzymes activities and inhibiting ROI generation.