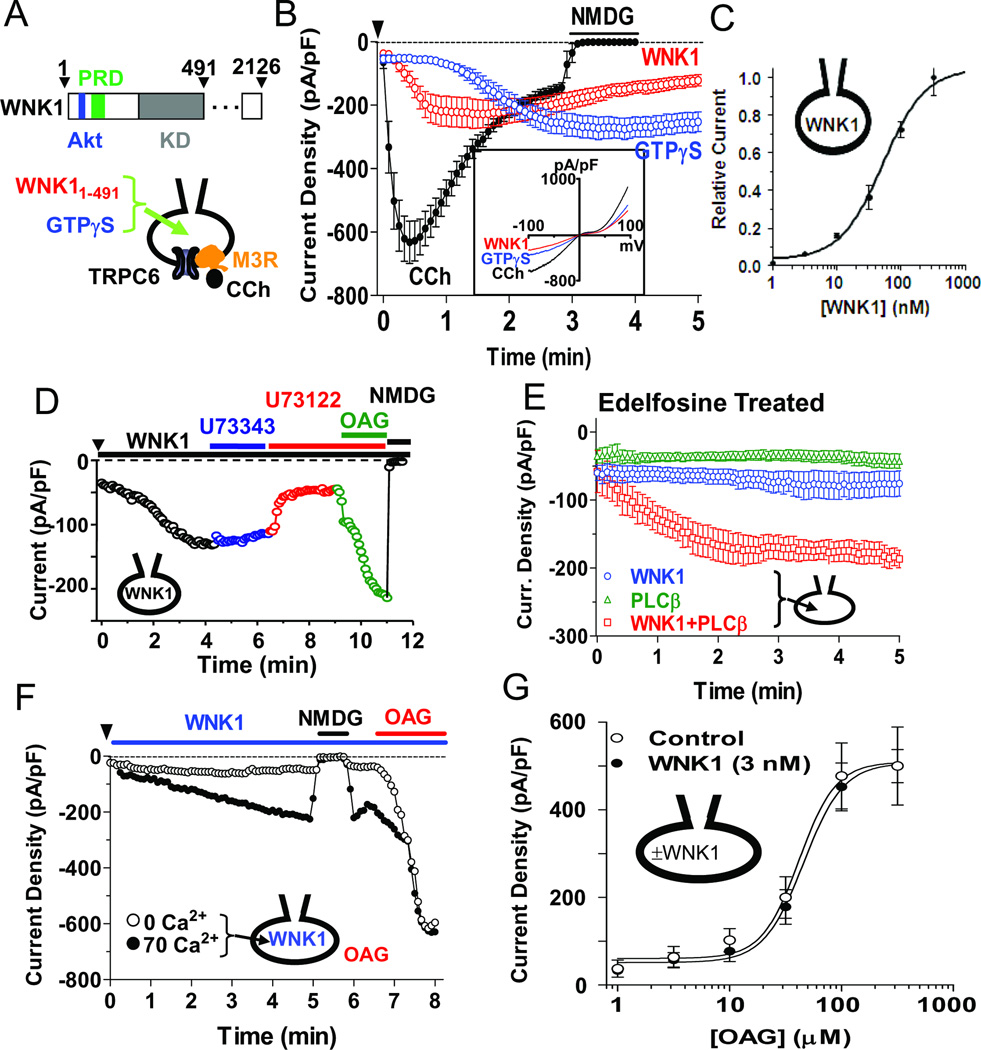
Figure 1.
Activation of TRPC6 by WNK1 requires PLC activity and is independent of WNK1 kinase activity. (A) Top: Domain structure of rat WNK1. Akt, its phosphorylation site; PRD, proline-rich domain; KD, kinase domain. Bottom: whole-cell patch-clamp recording of TRPC6. CCh: carbachol (100 µM); M3R: M3 muscarinic cholinergic receptor. Intracellular free [Ca2+] was 70 nM except as indicated in panel F. (B) Activation of TRPC6 by CCh via M3R, GTPγS or WNK11–491. HEK cells were transfected with TRPC6 with or without M3R. Data points (circles and error bars) are means ± SEM of inward current density (pA/pF at −100 mV; n = 5 for each). At the end of each recording, extracellular Na+ was replaced by the TRPC6-impermeable cation N-methyl-D-glucamine (NMDG) to gauge the background current. Inset shows current-voltage (I–V) relationships of activated TRPC6 currents. (C) Concentration-response curve for activation of TRPC6 by WNK11–491. (D) Effect of PLC inhibitor U73122 or inactive analog U73343 (2.5 µM each) on WNK11–491 activation of TRPC6. Inward current at −100 mV from a representative experiment. Similar results were observed in 6 independent experiments. (E) Cells were preincubated with 15 µM edelfosine for 1 hr and washed before recording. TRPC6 currents in response to 100 nM WNK11–491, 5 nM PLC-β1 or both were measured. (F) TRPC6 currents in response to WNK11–491 under 0 or 70 nM intracellular calcium. OAG was applied as indicated. (G) TRPC6 currents were measured in cells with or without intracellular application of 3 nM WNK11–491. OAG was applied to the extracellular solution at indicated concentrations. Although this concentration of WNK11–491 by itself does not activate TRPC6, it potentiated M3R activation of the channel (see Figure 3B). (see also Figure S1).