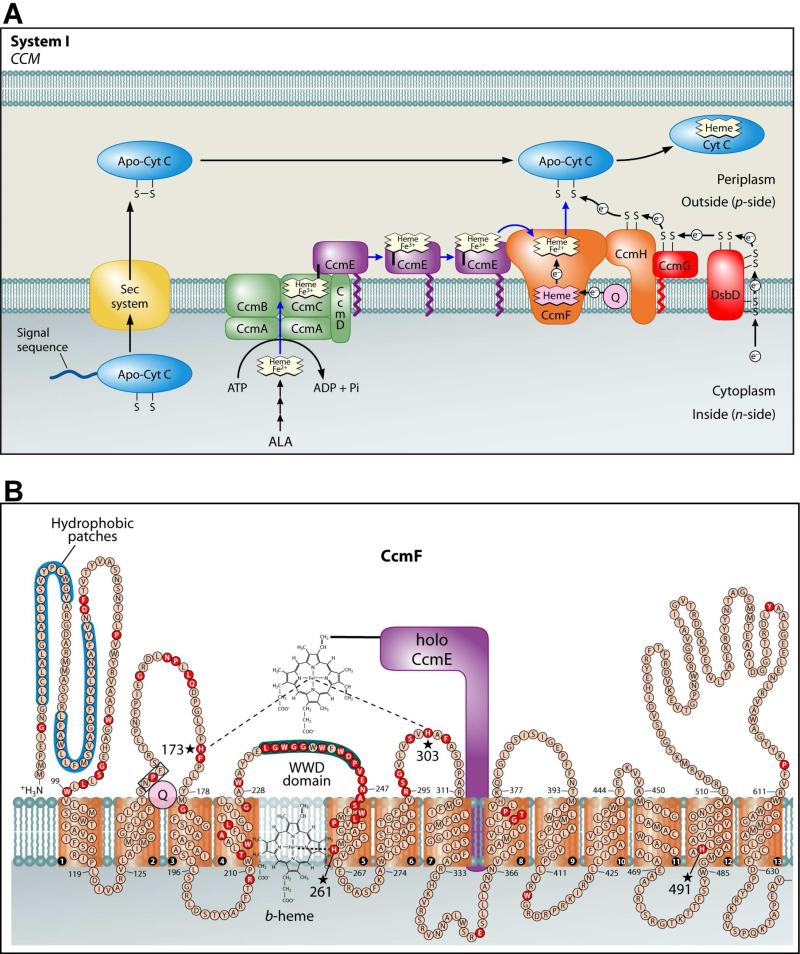
Figure 1.
Adapted from reference (5). (A) Current working model of the system I cytochrome c biogenesis pathway. Model includes trafficking and oxidation states of heme as well as the subpathways for apocytochrome translocation and reduction. (B) Topology of the CcmF integral membrane protein from E. coli. Possible histidine axial ligands to heme are starred. The highly conserved WWD domain is shaded as are the hydrophobic patches. Completely conserved amino acids (red) were identified by individual protein alignments using CcmF ORFs from the following organisms: the alpha proteobacteria, Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58, R. capsulatus, Caulobacter crescentus CB15, and Bradyrhizobium japonicum; the beta proteobacteria, Nitrospira mutliformis ATCC 25196 and Nitrosomonas europaea ATCC 19718; the gamma proteobacteria, E. coli K-12 MG1655, Pseudomonas fluorescens Pf01, Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 and Vibrio parahaemolyticus RIMD 2210633; the delta proteobacteria, Myxococcus xanthus and Desulfovibrio desulfuricans; and the deinococci, Deinococcus geothermalis and Thermus thermophilus.