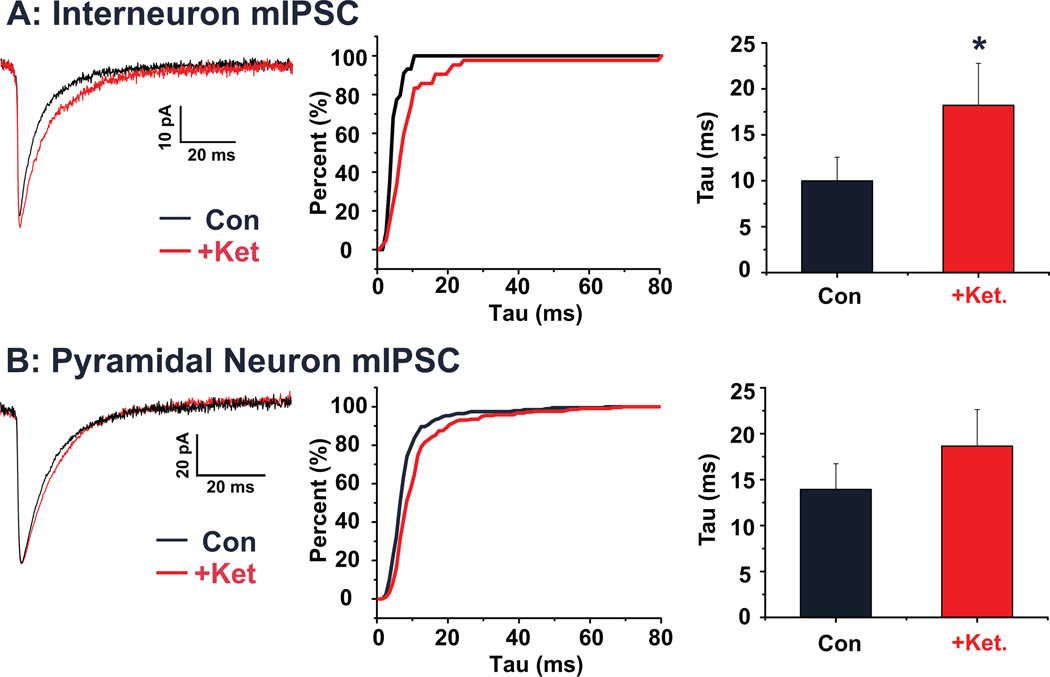
Figure 6. Acute ketamine increases mIPSC decay time in identified interneurons of the PrL.
(A) Average mIPSCs recorded from a representative PrL interneuron under control conditions (black) and following ketamine (red). The cumulative histogram plots the decay tau of interneuronal mIPSCs from the same representative cell under both control (black) and ketamine (red) treated conditions. Bar graph shows mean decay tau before and after ketamine application. Ketamine significantly (p < 0.05) increased the decay time. (B) Average mIPSCs recorded from a representative PrL pyramidal neuron under control conditions (black) and following ketamine (red). The cumulative histogram plots the decay tau of pyramidal mIPSCs from the same representative cell under both control (black) and ketamine (red) treated conditions. Bar graph shows mean decay tau before and after ketamine application. The increase in decay time in pyramidal neurons was not statistically significant. (* p < 0.05)