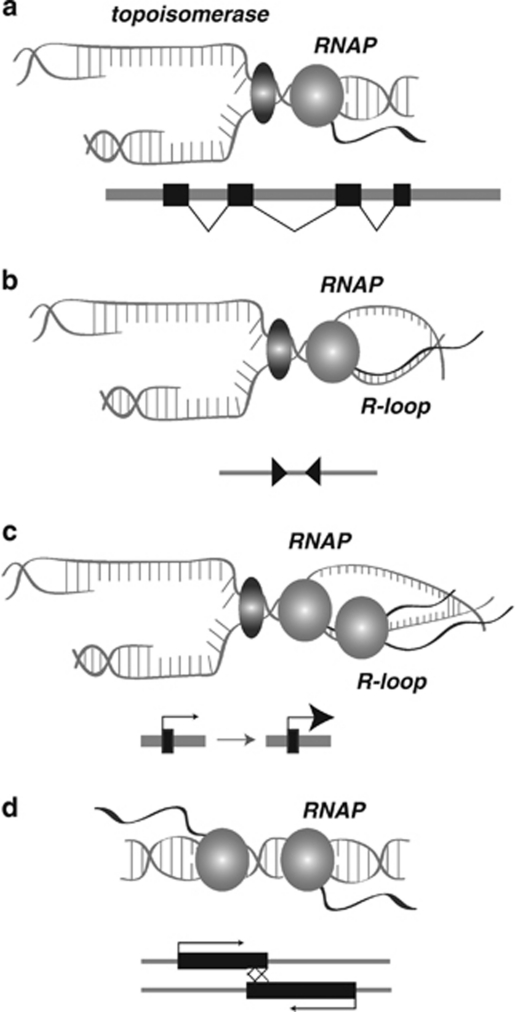
Figure 2.
Mechanisms of ncRNA facilitation of chromosome breaks. (a) Normal transcription and DNA replication proceed independently with no collisions. Topoisomerase (green) and RNAPII (light purple) run independently on the same segment of DNA. The gene structure is shown below, with exons as boxes and spliced introns indicated by lines. (b) An inverted duplication of two retroelements (or other ncRNA gene), shown at bottom as red triangles, causes recruitment of specific proteins (for example, Sap1) that cause a replication stall between the RNAP machinery and replication fork. This leads to the formation of an R-loop. (c) Increased transcription of a ncRNA (purple box with large arrowhead) leads to a buildup of RNAP, resulting in a replication stall and an R-loop. (d) Bidirectional ncRNA transcripts (purple) can also lead to a collision between two RNAP complexes. A full color version of this figure is available at the Heredity journal online.