Figure 8.
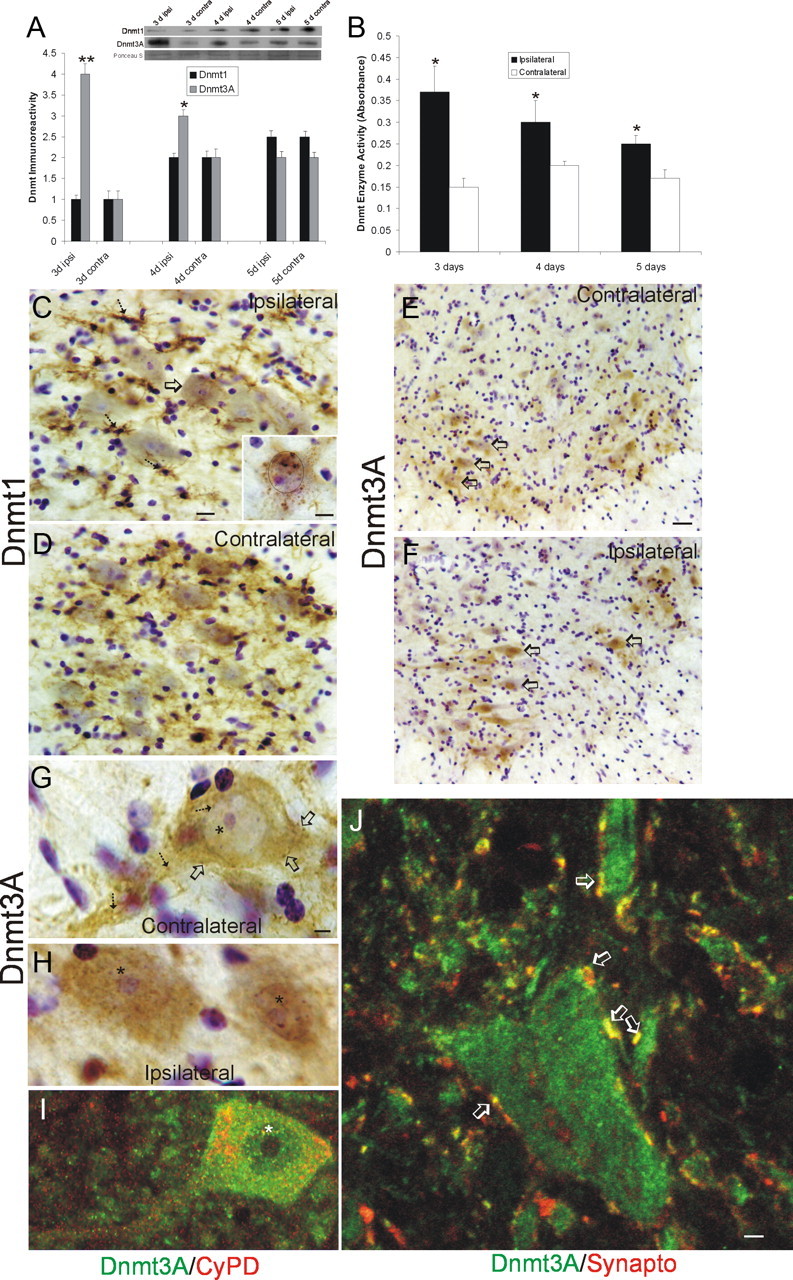
Dnmts are upregulated in adult mouse spinal cord during motor neuron apoptosis. A, Dnmt3a protein levels in spinal cord increase ipsilaterally after SNA. Adult mice received unilateral SNA, and 3, 4, and 5 d later (n = 4 per time), the lumbar spinal cords were microdissected into the nonlesioned contralateral control ventral horn (contra) and the lesioned ipsilateral ventral horn (ipsi). Crude homogenates were used for immunoblotting for Dnmt1 and Dnmt3a. Membranes were stained with Ponceau S to show protein loading. Values in graphs are mean ± SEM of optical density units. Asterisks denote a significant difference from contralateral for Dnmt3a at 3 d (p < 0.001) and 4 d (p < 0.05). See Figure 7B for basal levels of Dnmt1 and Dnmt3a in mature (P20) whole mouse spinal cord. B, Dnmt enzyme activity in spinal cord increases ipsilaterally after SNA. Adult mice received unilateral SNA, and 3, 4, and 5 d later (n = 4 per time), the lumbar spinal cords were microdissected into the nonlesioned contralateral control ventral horns (contra) and the lesioned ipsilateral ventral horns (ipsi). Crude homogenates were used for biochemical assessment of total Dnmt enzyme activity. Values in graphs are mean ± SD. Asterisks denote a significant difference from contralateral at 3 and 4 d (p < 0.01) and at 5 d (p < 0.05). C, D, Immunohistochemical localization of Dnmt1 in mouse lumbar spinal cord at 4 d after SNA. Dnmt1 immunoreactivity was visualized with diaminobenzedine (brown), and sections were counterstained with cresyl violet. C, The ipsilateral ventral horn showed Dnmt1 immunoreactivity within the cytoplasm and nucleus of motor neurons (arrow and inset) and in small cells resembling microglia (hatched arrows). Some motor neurons with chromatin condensation typical of apoptosis (as seen by cresyl violet counterstaining) displayed aggregates of Dnmt1 immunoreactivity in the nucleus and perinuclear region (inset; black circle delineates the nucleus). Scale bars: C (same for D), 20 μm; C, inset, 10 μm. D, In contrast, the contralateral ventral horn showed Dnmt1 immunoreactivity diffusely in the neuropil. E–H, Immunohistochemical localization of Dnmt3a in mouse lumbar spinal cord at 3 d after SNA as seen at low (E, F) and high (G, H) magnifications. Dnmt3a immunoreactivity was visualized with diaminobenzedine (brown), and sections were counterstained with cresyl violet. E, The contralateral control ventral horn showed Dnmt3a immunoreactivity within and around motor neurons (open arrows), but the nuclei of most motor neurons have low immunoreactivity in the nucleus. G, As seen at high resolution, Dnmt3a in normal motor neurons was seen faintly as diffuse immunoreactivity in the nucleus (asterisk) and in the cytoplasm as discrete puncta (hatched arrows). Pericellular bouton-like Dnmt3a immunoreactivity appeared in apposition to motor neurons (open arrows). F, H, In contrast, most ipsilateral motor neurons (F, open arrows) showed prominent Dnmt3a immunoreactivity in the nucleus (H, asterisks). Scale bars: in E (same for F), 20 μm; in G (same for H, I), 5 μm I, Confocal microscopy shows that some cytoplasmic Dnmt3a immunoreactivity in normal motor neurons is localized to mitochondria as demonstrated by its colocalization with the mitochondrial marker cyclophilin D (CyPD). Dnmt3a immunoreactivity is seen as green, and CyPD immunoreactivity is seen as red. Some cytoplasmic Dnmt3a immunoreactivity associates with mitochondria (seen as yellow), but single signals for Dnmt3a and CyPD can also be seen. Dnmt3a immunoreactivity is also seen in the nucleus (asterisk). J, Confocal microscopy shows that some Dnmt3a immunoreactivity is localized to presynaptic terminals as demonstrated by its colocalization with the presynaptic terminal marker synaptophysin. Dnmt3a immunoreactivity is seen as green, and synpatophysin (Synapto) immunoreactivity is seen as red. Perineuronal and peridendritic Dnmt3a is localized to axon terminals (hatched arrows, seen a yellow). Scale bar, 10 μm.
