Figure 3.
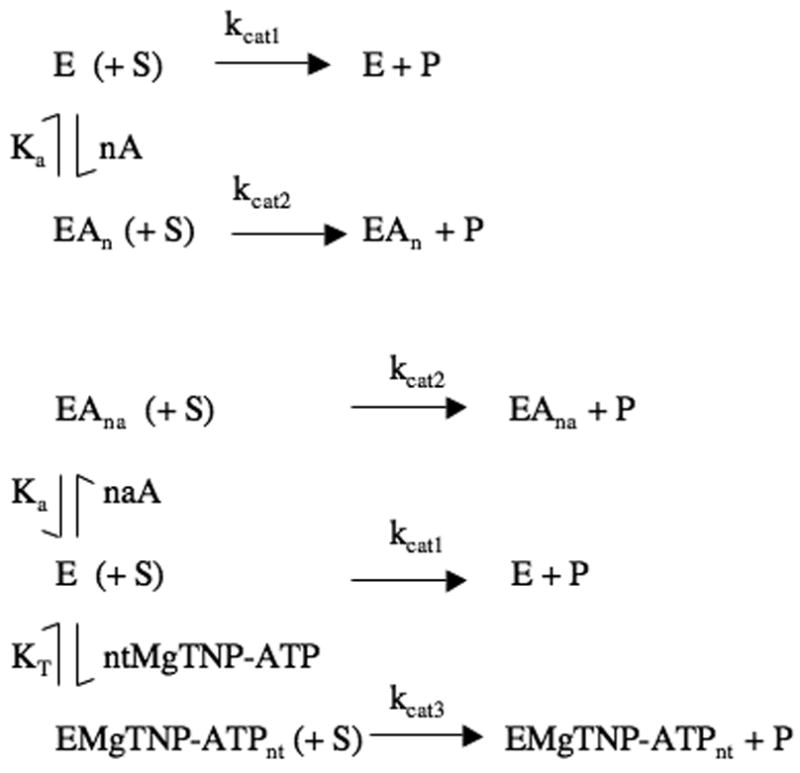
(a) Reaction scheme for the pyruvate carboxylation reaction in the presence of saturating substrates, accounting for the activation by acetyl CoA (A), where kcat1 and kcat2 are the catalytic rate constants for the reaction by the enzyme (E) and the enzyme-acetyl CoA complex (EAn) respectively. Ka is the apparent dissociation constant of the EAn complex and n is the Hill coefficient for the activation process. (b) Reaction scheme for the pyruvate carboxylation reaction in the presence of saturating substrates and both acetyl CoA and MgTNP-ATP, where kcat1, kcat2 and kcat3 are the catalytic rate constants for the reaction catalysed by the enzyme (E), the enzyme-acetyl CoA complex (EAna) and the enzyme-MgTNP-ATP complex (EMgTNP-ATPnt) respectively. Ka is the apparent dissociation constant of the EAn complex and na is the Hill coefficient for the activation by acetyl CoA. KT is the apparent dissociation constant of the EMgTNP-ATPnt complex and nt is the Hill coefficient for the activation by MgTNP-ATP.
