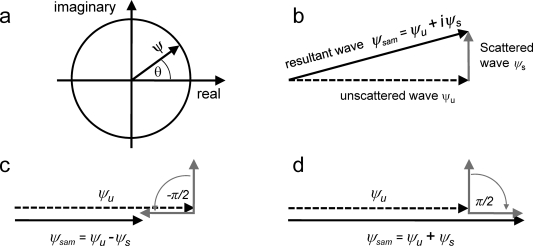
Figure 8.
Graphical representation of phase contrast. (a) Complex plane representation of a wave vector ψ with phase θ. (b) Vector representation of the scattered wave ψs, unscattered wave ψu, and resultant wave ψsam = ψu + iψs. Amplitudes (vector lengths) of ψsam and ψu are very similar, resulting in low image contrast. (c) −π/2 phase shift of the scattered wave leads to a noticeable decrease in the resultant wave amplitude relative to the unscattered wave (negative phase contrast). (d) π/2 phase shift of the scattered wave increases the amplitude of the resultant wave relative to the unscattered wave (positive phase contrast).