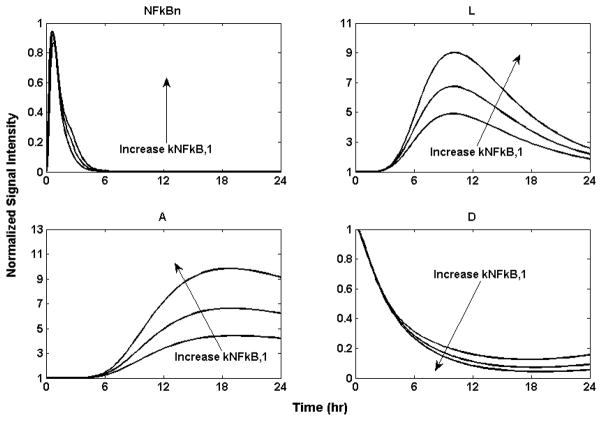
Figure 9.
Implication of dysregulation of NF-κB activity by increasing the activation rate of NF-κB by IKK signal kNFκ B,1 by 50% and 100% respectively. It leads to persistently elevated responses for “A” and “D”. The larger the NF-κB activation rate kNFκB,1, the higher the response will be for (L) the proinflammatory response, (A) the anti-inflammatory, and (D) the anabolism.