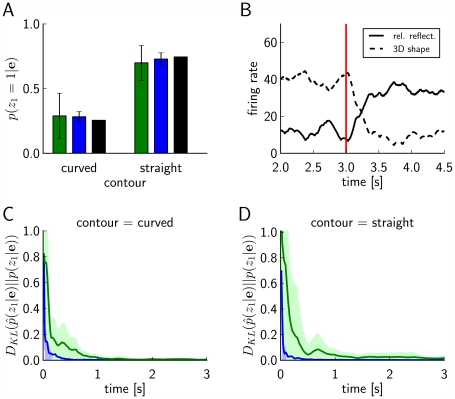
Figure 3. Results of Computer Simulation I.
Performance comparison between an ideal version of Implementation 1 (use of auxiliary RVs, results shown in green) and an ideal version of implementations that satisfy the NCC (results shown in blue) for probabilistic inference in the Bayesian network of Fig. 1B (“explaining away”. Evidence  (see (1)) is entered for the RVs
(see (1)) is entered for the RVs 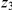 and
and 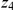 , and the marginal probability
, and the marginal probability  is estimated. A) Target values of
is estimated. A) Target values of  for
for  and
and 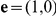 are shown in black, results from sampling for
are shown in black, results from sampling for  from a network of spiking neurons are shown in green and blue. Panels C) and D) show the temporal evolution of the Kullback-Leibler divergence between the resulting estimates through neural sampling
from a network of spiking neurons are shown in green and blue. Panels C) and D) show the temporal evolution of the Kullback-Leibler divergence between the resulting estimates through neural sampling  and the correct posterior
and the correct posterior 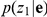 , averaged over 10 trials for
, averaged over 10 trials for  in C) and for
in C) and for 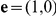 in D). The green and blue areas around the green and blue curves represent the unbiased value of the standard deviation. The estimated marginal posterior is calculated for each time point from the samples (number of spikes) from the beginning of the simulation (or from
in D). The green and blue areas around the green and blue curves represent the unbiased value of the standard deviation. The estimated marginal posterior is calculated for each time point from the samples (number of spikes) from the beginning of the simulation (or from 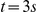 for the second inference query with
for the second inference query with 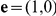 ). Panels A, C, D show that both approaches yield correct probabilistic inference through neural sampling, but the approach via satisfying the NCC converges about 10 times faster. B) The firing rates of principal neuron
). Panels A, C, D show that both approaches yield correct probabilistic inference through neural sampling, but the approach via satisfying the NCC converges about 10 times faster. B) The firing rates of principal neuron  (solid line) and of the principal neuron
(solid line) and of the principal neuron  (dashed line) in the approach via satisfying the NCC, estimated with a sliding window (alpha kernel
(dashed line) in the approach via satisfying the NCC, estimated with a sliding window (alpha kernel 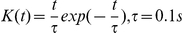 ). In this experiment the evidence
). In this experiment the evidence  was switched after 3 s (red vertical line) from
was switched after 3 s (red vertical line) from 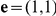 to
to 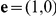 . The “explaining away”effect is clearly visible from the complementary evolution of the firing rates of the neurons
. The “explaining away”effect is clearly visible from the complementary evolution of the firing rates of the neurons  and
and 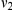 .
.